Bacillus licheniformis is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, facultative anaerobic bacterium commonly found in soil, water, and on plant surfaces. It is closely related to Bacillus subtilis and is known for its ability to produce enzymes and antimicrobial compounds. Here are some key details:
1.Scientific Classification:
- Kingdom: Bacteria
- Phylum: Firmicutes
- Class: Bacilli
- Order: Bacillales
- Family: Bacillaceae
- Genus: Bacillus
- Species: Bacillus licheniformis

2.Morphology:
- Gram-positive, rod-shaped
- Forms endospores, allowing it to survive harsh conditions
- Motile due to peritrichous flagella
3.Habitat:
- Found in soil, water, and decaying organic matter
- Can be isolated from food and industrial environments
4.Physiological Characteristics:
- Facultative anaerobe (can grow with or without oxygen)
- Optimal growth temperature: 30–50°C (mesophilic to moderately thermophilic)
- Produces extracellular enzymes such as proteases, amylases, and lipases
5.Applications:
- Industrial Enzyme Production: Produces proteases (e.g., subtilisin), amylases, and lipases used in detergents, food, and textile industries.
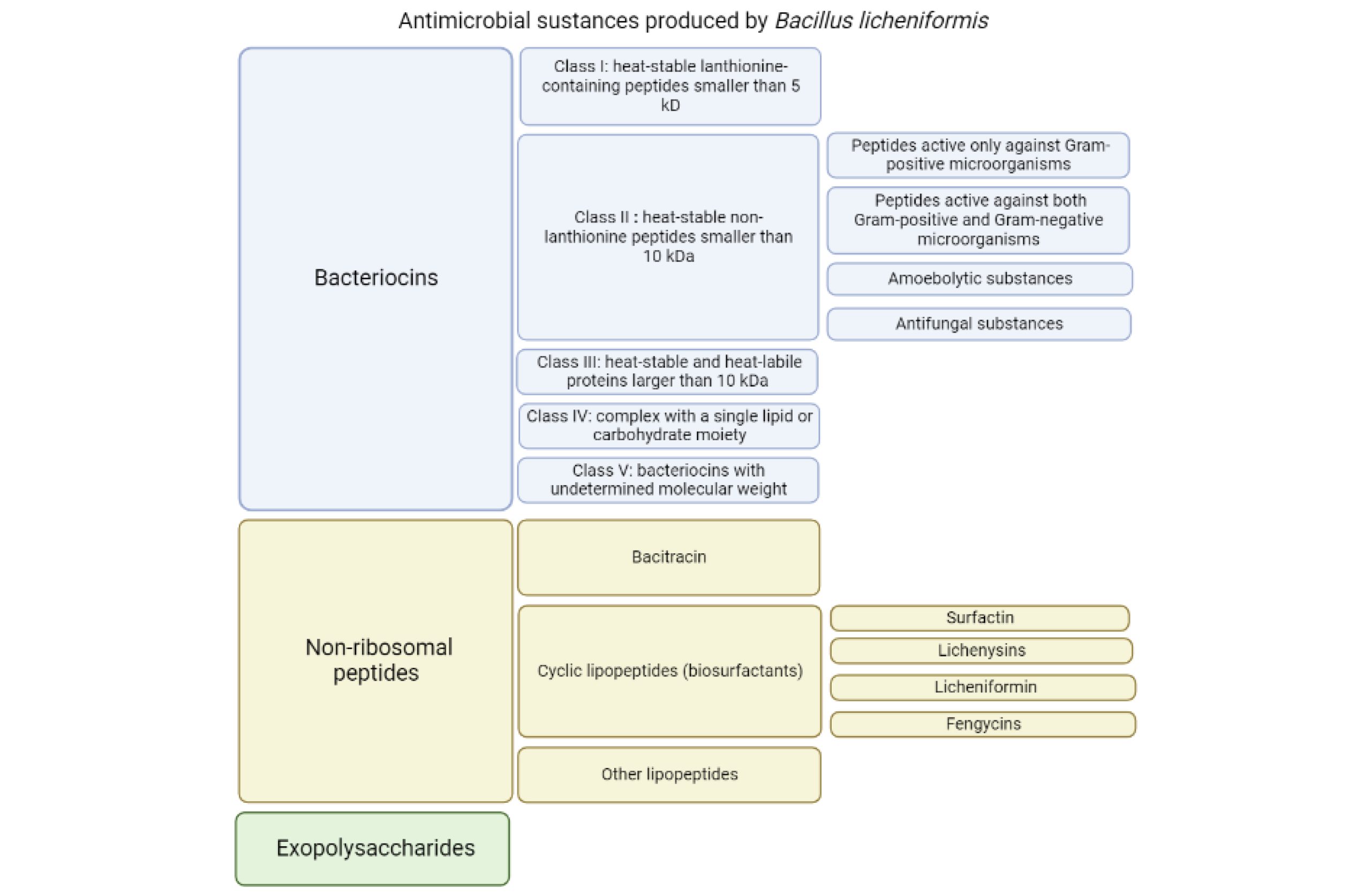
- Antibiotic Production: Produces bacitracin, an antimicrobial peptide.
- Bioremediation: Used for breaking down organic waste.
- Probiotics and Agriculture: Used as a probiotic in animal feed to promote gut health and improve digestion.
6.Pathogenicity:
- Generally considered non-pathogenic, but may cause food spoilage and rare opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals.
Would you like more details on a specific aspect of Bacillus licheniformis?
