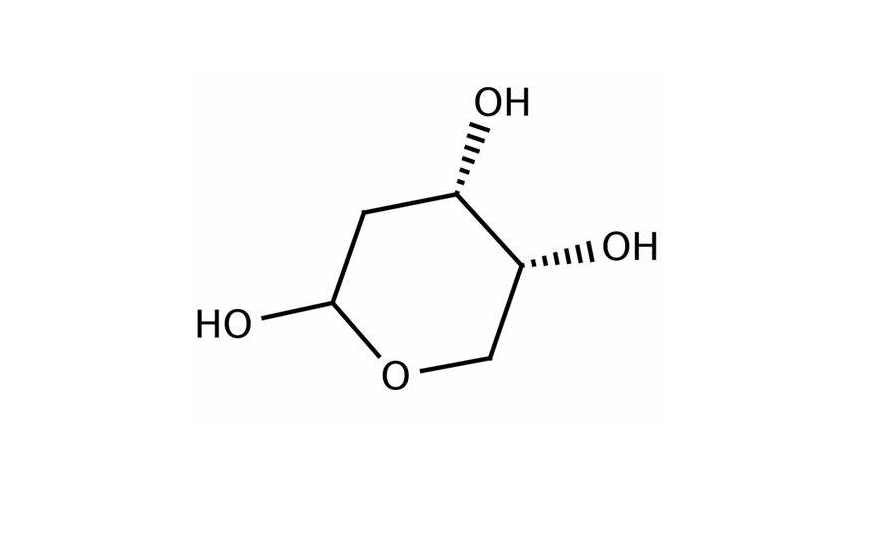
2-Deoxy-D-Ribose is a sugar molecule, specifically a monosaccharide, which is a type of simple sugar. It is a modified version of D-Rbose, a naturally occurring sugar found in RNA (ribonucleic acid). The key difference between D-Ribose and 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose is that 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose lacks an oxygen atom at the 2′ carbon position of the ribose molecule, hence the name “2-deoxy.”
Here’s a breakdown of its structure:
- Carbon atoms: 5 carbon atoms, which form a backbone.
- Hydroxyl groups (-OH): Attachments at various positions on the carbon atoms.
- Hydrogen atom (H): At the 2′ carbon in place of the hydroxyl group in D-ribose.
The molecular formula of 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose is C5H10O4. This sugar is crucial in the structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), where it forms the backbone of the DNA strand.
Adverse effects of 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose
2-Deoxy-D-Ribose is a sugar analog that has been researched primarily for its potential in cancer therapy and metabolic disorders due to its ability to interfere with the energy production pathways in cells. While it has shown promise in various studies, especially in the context of its anti-cancer and anti-viral properties, it can also have some adverse effects, especially when used at higher doses or over long periods of time. These potential side effects include:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Since 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose interferes with cellular energy production, it may lead to fatigue, weakness, or general low energy, especially in normal, healthy cells that rely on glucose metabolism for energy.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal discomfort is another potential side effect, including nausea and vomiting, which can occur due to the disruption in normal cellular processes.
- Headache: Some users report headaches, likely due to the impact 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose has on metabolic pathways in the brain and nervous system.
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Because 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose mimics glucose, it may cause a drop in blood sugar levels, leading to hypoglycemia, particularly if the individual is also taking medications that lower blood sugar or has pre-existing conditions affecting glucose metabolism.
- Dizziness: Related to blood sugar changes and the metabolic disruption that can occur with 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose use, some individuals may experience dizziness.
- Tissue Damage: In higher doses, 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose has the potential to cause cellular damage. The interference with normal glucose metabolism could harm both cancerous and healthy cells, depending on the dose and duration of use.
- Potential for Long-Term Health Effects: The long-term effects of using 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose have not been fully established. There could be risks associated with prolonged interference in cellular energy production, though more research is needed to fully understand these potential risks.

Because 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose is often used in experimental settings or clinical trials, the dosing and safety profile might be closely monitored, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before using it outside of a controlled environment.
If you’re considering 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose for any health-related reason, it’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and ensure it’s used under medical supervision.
