2-Deoxy-D-Ribose is a sugar molecule that is similar to D-ribose but lacks one hydroxyl group at the 2′ position of the ribose ring. It plays a key role in the structure of DNA, as it forms the backbone of the nucleic acids by linking to phosphate groups.
Chemical Structure of 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose:
The chemical formula for 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose is C₅H₁₀O₄, and its structure can be represented as follows:
- It has a five-membered carbon ring (like ribose) with the hydroxyl group (-OH) on carbons 3, 4, and 5.
- At the 2′ position, there is a hydrogen atom (instead of a hydroxyl group, which is present in ribose).
The structure is often depicted as follows:
2-Deoxy-D-Ribose has the following structural components:
- Carbon atoms labeled as C1′, C2′, C3′, C4′, and C5′.
- The hydroxyl groups (-OH) are located on C3′, C4′, and C5′, and a hydrogen atom (-H) is attached to C2′.
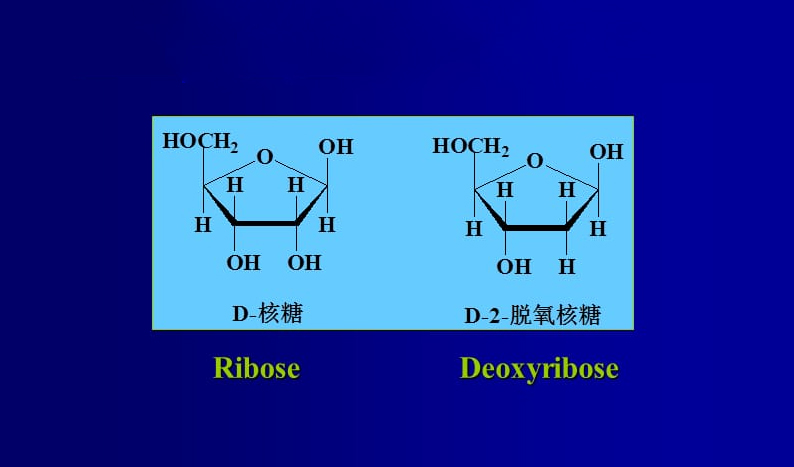
In the Fischer projection, the structure looks like this:
HOCH2
|
HO – C – H
|
HO – C – H
|
C – H
|
CH2OH
Physical Properties of 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose:
- Molecular Weight: 150.13 g/mol.
- Melting Point: 95–100°C.
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, due to the hydroxyl groups and its ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
- Appearance: A white, crystalline solid, typically in the form of a powder.

Key Features:
- The absence of a hydroxyl group at the 2′ position distinguishes 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose from its close relative D-ribose, which is important for its role in DNA rather than RNA (where ribose is used).
- It has a role in the backbone of DNA molecules, linking with phosphate groups to form the nucleotide chain.
Would you like to know more about its biological significance or any other details?
