5-Deazaflavin and NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) are both compounds that have gained attention for their potential health benefits, though they work through different mechanisms and have distinct roles in the body. Here’s a comparison between the two:
1. 5-Deazaflavin
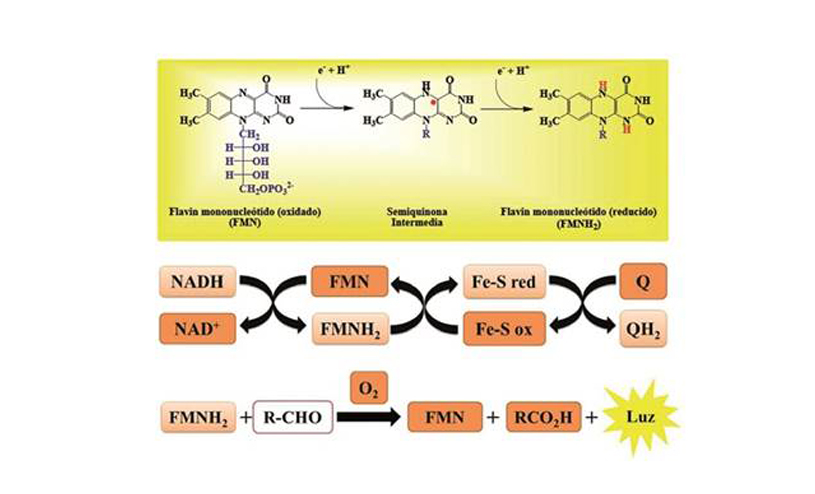
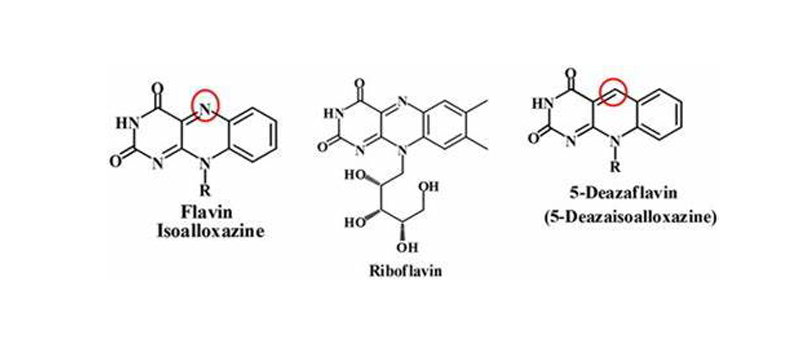
Structure & Origin: 5-Deazaflavin is a synthetic derivative of flavin mononucleotide (FMN), which is a coenzyme form of riboflavin (Vitamin B2). It plays a role in various enzymatic processes in the body, particularly in reactions involving redox reactions and electron transfers.
Potential Uses:
- 5-Deazaflavin is being researched for its role in mitochondrial function, as it may have a significant impact on cellular energy production and efficiency.
- It has been suggested as a potential therapeutic agent for diseases related to mitochondrial dysfunction, including neurodegenerative diseases.
- Research into its antioxidant properties and potential benefits for aging and longevity is ongoing.
Mechanism of Action: 5-Deazaflavin is thought to act through mitochondrial processes, improving energy production by enhancing electron transport and reducing oxidative stress.
2. NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
Structure & Origin: NMN is a naturally occurring compound in the body and a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a vital coenzyme involved in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular aging.
Potential Uses:
- NMN supplementation is often touted for its potential anti-aging effects, primarily because it helps boost NAD+ levels, which naturally decline with age.
- Increasing NAD+ levels may support mitochondrial function, improve energy levels, enhance metabolism, and promote healthy aging.
- It’s being investigated for its potential to improve cognitive function, protect against neurodegenerative diseases, and enhance physical endurance.
Mechanism of Action: NMN works by increasing NAD+ levels in cells, which in turn supports various cellular processes like energy production, DNA repair, and regulation of gene expression related to longevity.
Key Differences:
Primary Mechanism:
- 5-Deazaflavin works more directly on mitochondrial efficiency and electron transport, while NMN works indirectly by increasing NAD+ levels, which are critical for cellular energy and metabolic functions.
Health Focus:
- 5-Deazaflavin is benefits are more focused on mitochondrial function and potentially improving cellular energy production, with some research indicating neuroprotective effects.
- NMN is primary role is boosting NAD+ levels to support aging processes, energy metabolism, and overall cellular health, with a broad range of longevity-related research.
Research Stage:
- While both are in the research phase, NMN has been more extensively studied for anti-aging and health benefits, while 5-Deazaflavin is still more experimental and less well-known in terms of its practical applications.
Summary:
- 5-Deazaflavin: Primarily researched for its impact on mitochondrial function and energy production.
- NMN: Focused on increasing NAD+ levels for overall cellular health, metabolism, and aging-related benefits.
Each compound has promising potential, but they address different aspects of cellular health and metabolism. If you’re considering supplementation for anti-aging or energy, NMN is the more widely studied option. However, 5-Deazaflavin may have niche benefits for mitochondrial health and efficiency.
