Benfotiamine (S-benzoylthiamine-O-monophosphate) is a synthetic, lipid-soluble thiamine derivative.
Chemical structure of Benfotiamine
- Core is thiamine (vitamin B1)
- Has a benzoate group on the sulfur → ↑ lipophilicity
- Has a phosphate group → prodrug behaviour
Formula: C₁₉H₂₃N₄O₆PS
Exact mass: ~470.45 g/mol
IUPAC: S-benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate
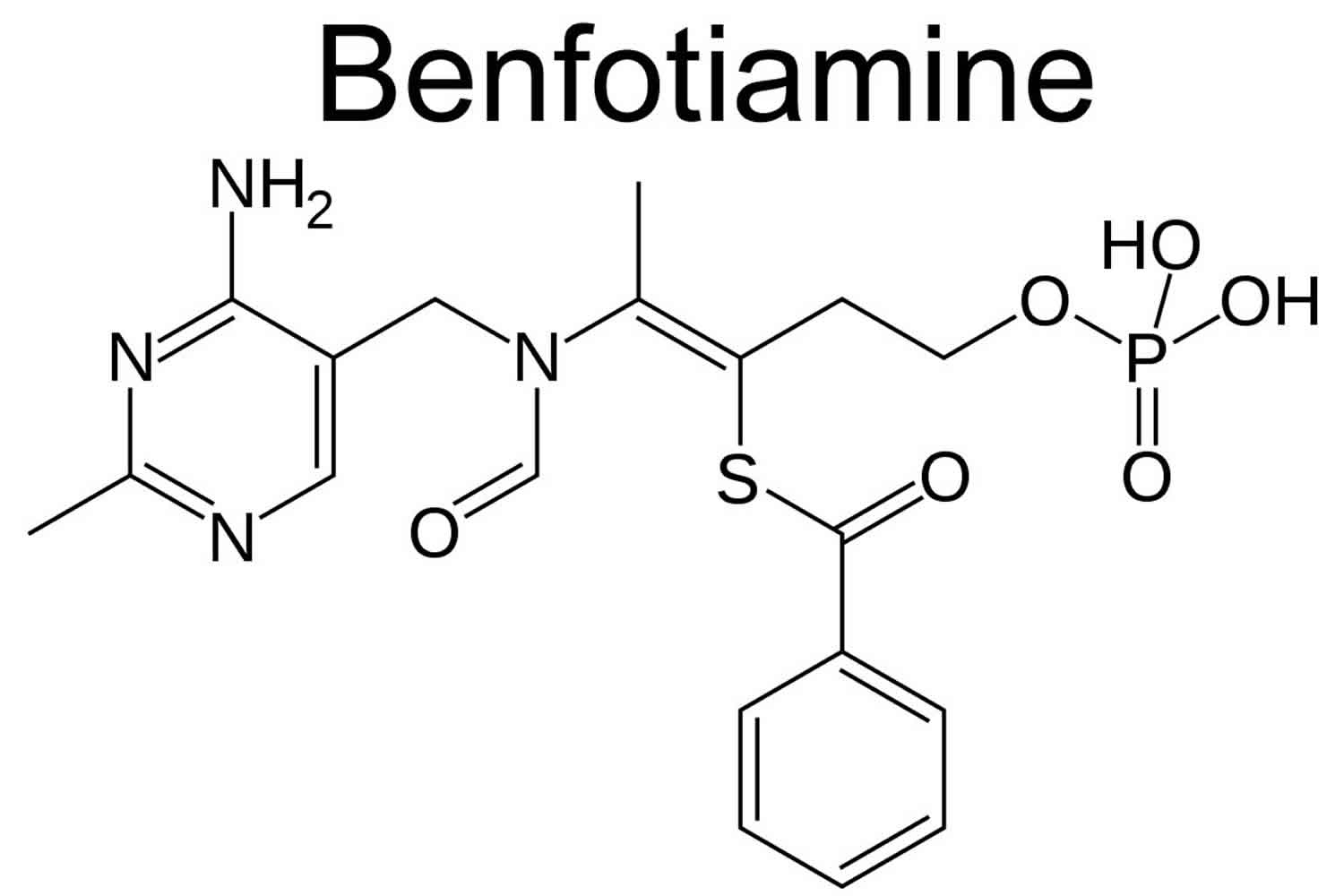
The benzoyl group is the key — this blocks water-loving ionic sites → this is why Benfotiamine is fat-soluble (standard thiamine is water soluble).
Once absorbed, alkaline phosphatases cleave off the phosphate → the active species is S-benzoylthiamine, then it is converted further into thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), the active coenzyme.
Physical properties of Benfotiamine
| Property | Data |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Molecular weight | 470.45 g/mol |
| Solubility | Lipophilic; slightly soluble in water, soluble in organic solvents (ethanol etc) |
| Stability | Relatively stable at room temperature; protected form of thiamine (thiamine itself is unstable in heat/alkaline) |
| Bioavailability | >5× oral bioavailability vs thiamine HCl (human oral PK data) |
| PKa | Behaves neutrally at physiological pH because it has no free protonated thiazolium (protected) |

Why the structure matters
- Thiamine hydrochloride is charged → poor passive diffusion
- Benfotiamine is protected and neutral → significant passive diffusion through membranes
→ Mechanistic result: higher tissue thiamine activation (higher TPP in cells), especially nerve cells.
In very simplified form:
Benfotiamine = “coated” thiamine → fat soluble → easier body entry → then metabolic enzymes take off the coat inside.
