Boron Nitride (BN) and Boron Carbide (B₄C) — two advanced ceramic materials often used for high-performance applications but with very different structures and properties.
1. Chemical Composition
Boron Nitride (BN):
Composed of boron (B) and nitrogen (N) atoms.
Boron Carbide (B₄C):
Composed of boron (B) and carbon (C) atoms.
2. Crystal Structure
Boron Nitride (BN):
Comes in several forms, similar to carbon:
- h-BN (hexagonal BN): graphite-like, soft, lubricating
- c-BN (cubic BN): diamond-like, extremely hard
- w-BN (wurtzite BN): even harder than diamond in certain directions
B₄C:
Has a rhombohedral crystal structure, very hard and resistant to wear.
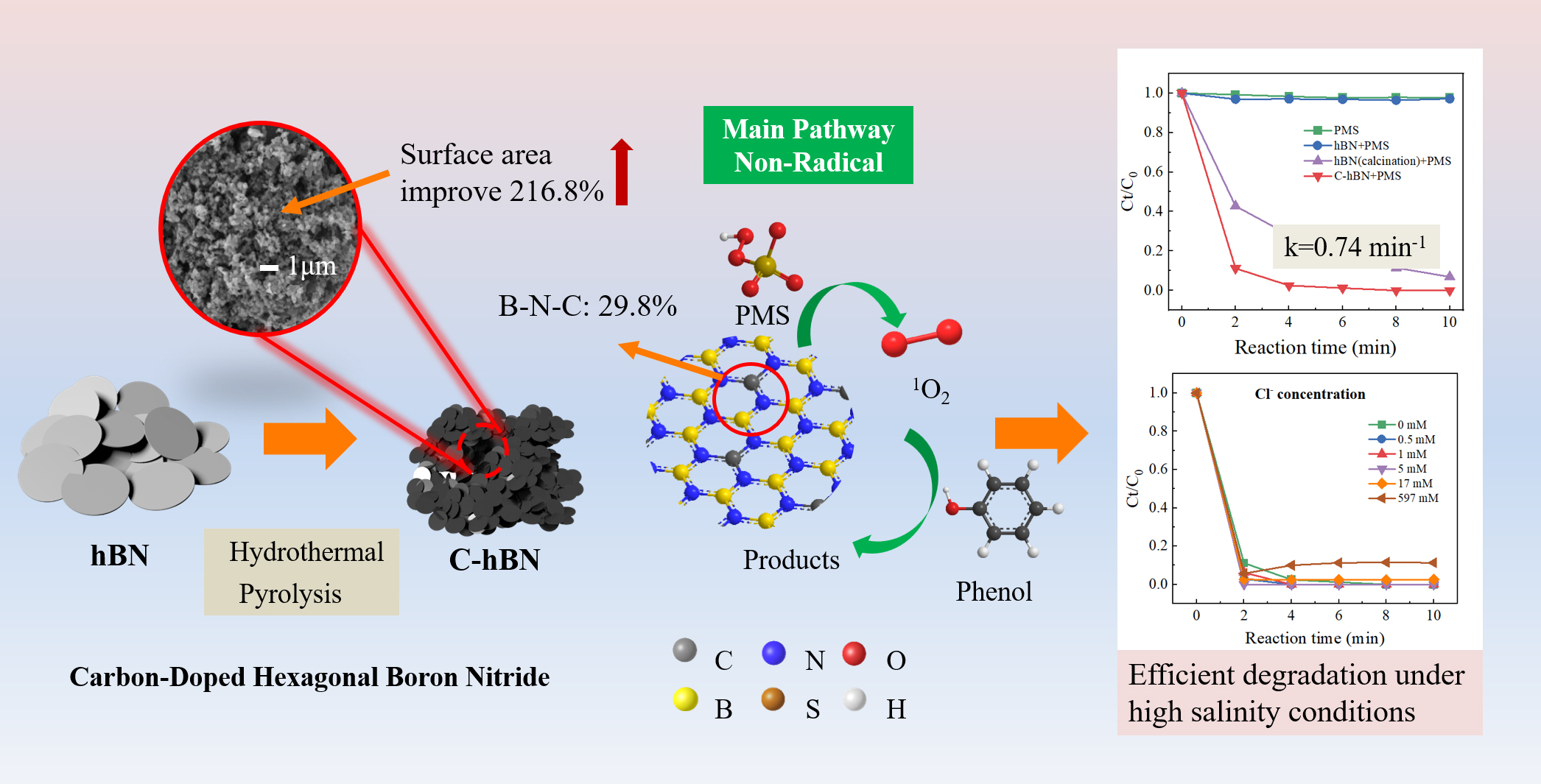
3. Hardness
Boron Nitride (BN):
- c-BN is the second hardest material after diamond
- h-BN is soft (like graphite)
B₄C:
One of the hardest known materials (ranking just below c-BN and diamond)
Hardness ranking (approx):
Diamond > w-BN ≥ c-BN > Boron Carbide > Silicon Carbide
4. Thermal Properties
Boron Nitride (BN):
- High thermal conductivity
- Excellent heat resistance (stable up to ~1000°C in air)
- Good thermal shock resistance
B₄C:
- Lower thermal conductivity than BN
- High melting point (~2450°C)
- Strong but poorer thermal shock resistance compared to Boron Nitride
5. Electrical Properties
Boron Nitride (BN):
Excellent electrical insulator, used in electronics and high-temperature insulators.
B₄C:
Semiconducting properties, slightly electrically conductive.
6. Chemical Stability
Boron Nitride (BN):
Chemically inert, resistant to most acids and bases.
B₄C:
Good chemical stability but reacts with strong oxidizers or hot concentrated alkalis.
7. Typical Applications
Boron Nitride (BN):
- Lubricants (h-BN, “white graphite”)
- High-temperature crucibles and furnace parts
- Electrical insulators
- Thermal management materials
- Coatings for metal casting
Boron Carbide (B₄C):
- Armor (bulletproof vests, tank armor)
- Abrasives (sandblasting, grinding)
- Neutron absorbers in nuclear reactors
- Wear-resistant materials
- Cutting tools (though less common than c-BN)
8. General Summary
| Property | Boron Nitride (BN) | Boron Carbide (B₄C) |
| Composition | B + N | B + C |
| Forms | Hexagonal, Cubic, Wurtzite | One main rhombohedral form |
| Hardness | Varies: soft (h-BN) to extremely hard (c-BN) | Very hard |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Moderate |
| Electrical Conductivity | Insulator | Semiconductor |
| Chemical Stability | Very high | High |
| Main Uses | Lubricants, insulators, high-temp ceramics | Armor, abrasives, neutron absorption |
