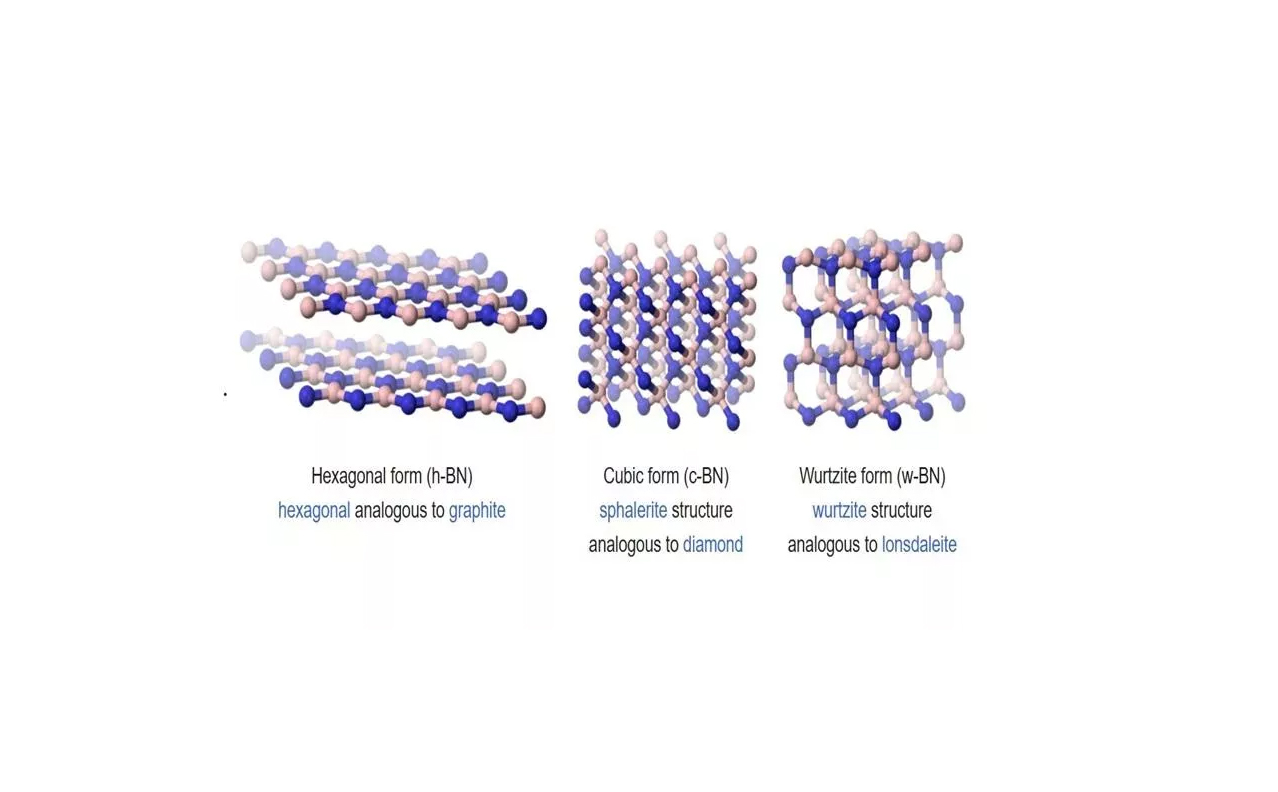
Boron Nitride is a chemical compound made of boron (B) and nitrogen (N) with the formula Boron Nitride(BN). It is a synthetic material with several crystalline forms, each with unique properties.
Pros of Boron Nitride:
1. High Thermal Stability
- Boron Nitride can withstand very high temperatures (up to ~900–1,500°C in air, higher in inert atmospheres) without significant degradation.
- Useful in high-temperature coatings, crucibles, and thermal management applications.
2. Excellent Thermal Conductivity
- Particularly in its hexagonal form (h-BN), it has high in-plane thermal conductivity while remaining electrically insulating.
- Ideal for heat dissipation in electronics without causing electrical shorts.

3. Electrical Insulation
- Boron Nitride is an excellent electrical insulator.
- Commonly used in electronics, semiconductors, and insulating components in high-voltage applications.
4. Chemical Inertness
- Resistant to chemical attack by acids, alkalis, and molten metals.
- Suitable for protective coatings and chemical-resistant components.
5. Lubricating Properties
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride has a layered structure similar to graphite, giving it excellent dry lubrication properties.
- Works under extreme temperatures and pressures where oils or greases fail.
6. Low Density and Lightweight
- Boron Nitride is relatively light, making it attractive for aerospace and advanced materials applications.
7. Radiation Resistance
- Stable under neutron radiation, making it useful in nuclear applications.
8. Versatility in Forms
- Available as powders, coatings, thin films, composites, and ceramics.
- Can be tailored for thermal, mechanical, or lubricating applications.
Cons of Boron Nitride:
1. Cost
- Boron Nitride can be expensive compared to conventional ceramics or lubricants, limiting its use in cost-sensitive applications.
2. Brittleness
- Like most ceramics, Boron Nitride is brittle and can fracture under mechanical stress, especially in its cubic or hexagonal crystalline forms.
3. Limited Mechanical Strength
- Its strength is lower compared to materials like boron carbide or silicon carbide.
- Not suitable for structural load-bearing components.
4. Processing Challenges
- High-purity Boron Nitride can be difficult to synthesize and process.
- Requires high-temperature sintering or chemical vapor deposition for high-performance applications.
5. Moisture Sensitivity (in some forms)
- Some Boron Nitride powders or composites can absorb moisture, which may affect certain applications, such as in electronics or high-temperature coatings.
6. Not a Metal Substitute
- Boron Nitride is electrically insulating; it cannot replace metals in conductive or structural applications.
Summary Table:
| Pros | Cons |
| High thermal stability | High cost |
| Excellent thermal conductivity | Brittle, low mechanical strength |
| Electrical insulation | Processing challenges |
| Chemical inertness | Moisture sensitivity in some forms |
| Lubricating properties | Not electrically conductive |
| Lightweight | Limited structural applications |
| Radiation resistant | |
| Versatile forms |
