Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol (DMC) is primarily known as a potent antioxidant compound, structurally related to vitamin E analogs. While it is mostly studied in cosmetic and dermatological contexts, its medical applications are emerging due to its ability to neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative stress.
Applications of Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol in Medicine
1. Neuroprotection
- Mechanism: Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), reducing oxidative damage in neurons.
- Potential Use: Could be explored in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke-related damage.
- Supporting Evidence: In vitro studies suggest Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol reduces lipid peroxidation and neuronal apoptosis.
2. Cardiovascular Protection
- Mechanism: Prevents oxidative modification of LDL cholesterol and endothelial damage.
- Potential Use: Could reduce risk factors associated with atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease.
- Supporting Evidence: Antioxidant properties may support vascular health by preserving nitric oxide levels and improving endothelial function.
3. Anti-inflammatory Effects
- Mechanism: By reducing oxidative stress, Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol indirectly suppresses inflammatory pathways (e.g., NF-κB activation).
- Potential Use: Could be used in chronic inflammatory conditions or as an adjunct in diseases like arthritis.
- Supporting Evidence: Early studies show lowered pro-inflammatory cytokines in oxidative stress models.
4. Hepatoprotection
- Mechanism: Protects liver cells from oxidative damage caused by toxins, drugs, or metabolic stress.
- Potential Use: May help in drug-induced liver injury or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Supporting Evidence: Animal studies demonstrate decreased liver enzyme markers and reduced lipid peroxidation.
5. Skin-related Therapeutics
- Mechanism: Limits oxidative damage to skin cells, inhibits UV-induced free radical formation.
- Medical Use: Beyond cosmetic anti-aging, it could assist in photoaging prevention and wound healing.
- Supporting Evidence: Demonstrated reduction in markers of oxidative stress in dermal cells exposed to UV radiation.
6. Adjunct in Cancer Therapy
- Mechanism: Protects normal cells from chemotherapy-induced oxidative stress without interfering with drug efficacy.
- Potential Use: May serve as a cytoprotective agent during cancer treatments.
- Supporting Evidence: Preclinical studies suggest reduced side effects like cardiotoxicity when antioxidants are co-administered with chemotherapy.
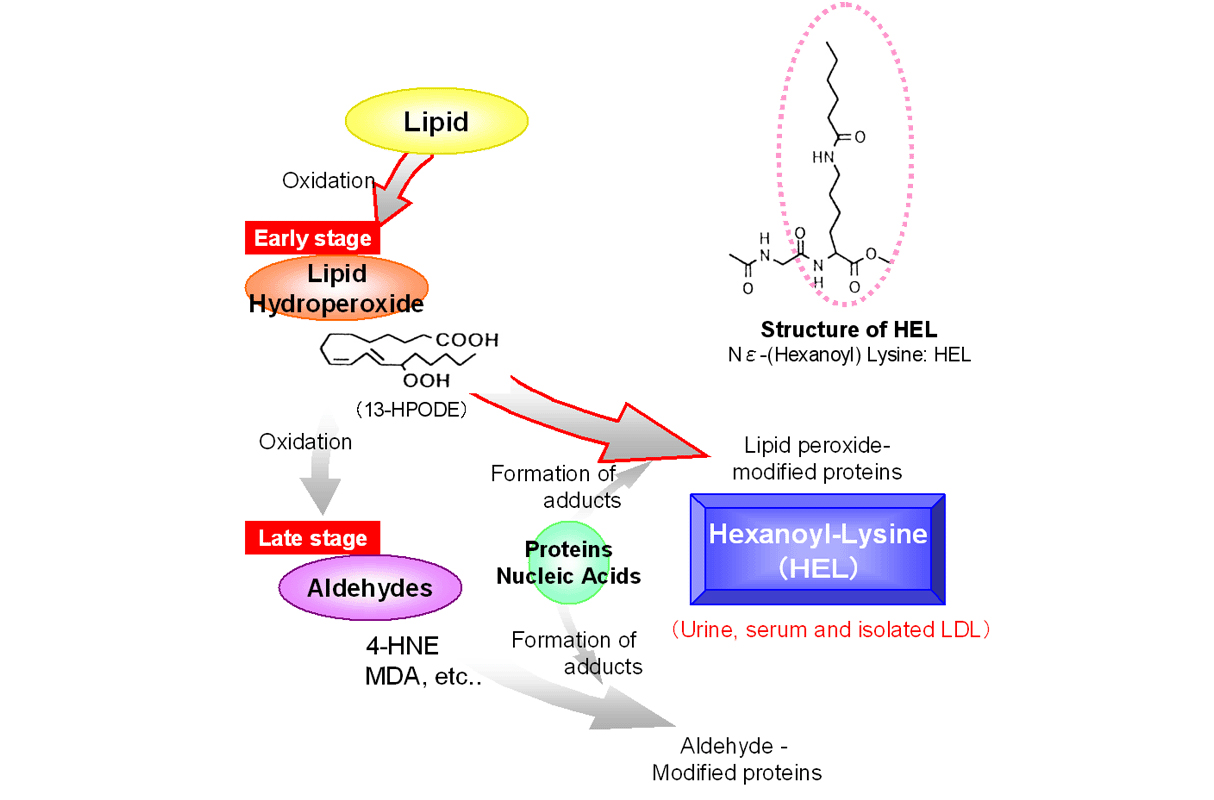
7. Potential Anti-diabetic Effects
- Mechanism: Oxidative stress plays a role in insulin resistance and beta-cell damage; Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol may mitigate this.
- Potential Use: Could complement therapy for type 2 diabetes.
- Supporting Evidence: Early animal studies indicate improved oxidative markers and pancreatic cell protection.
Summary:
While Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol is mostly recognized in cosmetic formulations for its antioxidant and anti-aging benefits, its medical potential is broad, including neuroprotection, cardiovascular support, anti-inflammatory activity, liver protection, and adjunctive roles in cancer or diabetes management. However, most applications are still preclinical or experimental, and human clinical trials are limited.
