�� What is Boron Nitride?
Boron Nitride (BN) is a synthetic chemical compound made of boron (B) and nitrogen (N) atoms in a 1:1 ratio.
It is sometimes called “white graphite” because one of its forms resembles graphite in structure and properties.
�� Chemical Basics
- Chemical formula: Boron Nitride (BN)
- Composition: Boron + Nitrogen
- Molar mass: ~24.82 g/mol
- Appearance: White, odorless, non-toxic powder or solid
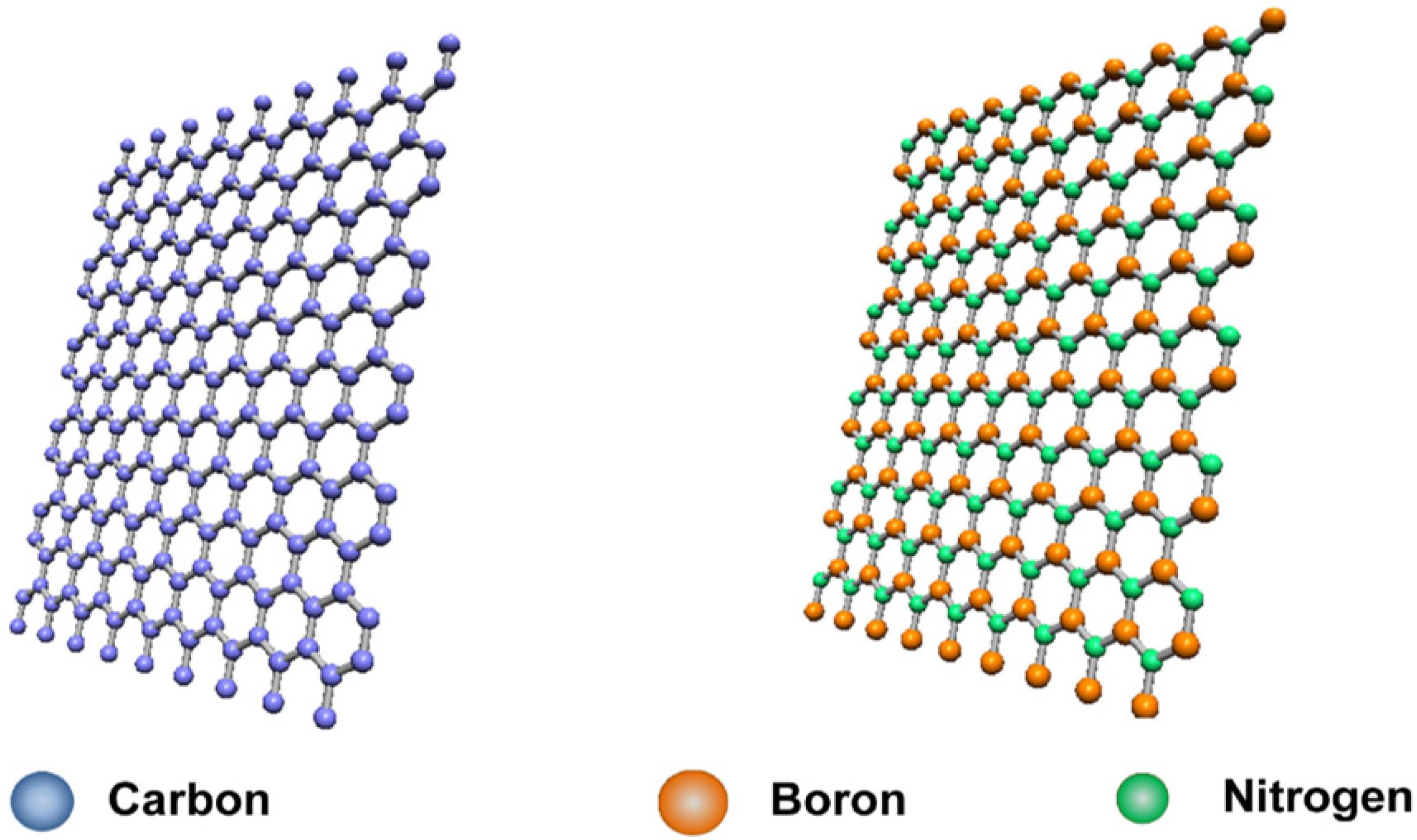
�� Main Crystal Forms
Boron Nitride exists in several structural forms (polymorphs):
1. Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN)
- Most common form
- Layered structure → similar to graphite
- White, soft, slippery
- Used as lubricant, thermal filler, cosmetic ingredient, etc.
2. Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN)
- Structure similar to diamond
- Extremely hard (second only to diamond)
- Used as cutting tools, abrasives
3. Wurtzite Boron Nitride (w-BN)
- Rare and very hard
- Formed under extreme pressure and temperature
�� Key Properties
- High thermal conductivity
- Excellent electrical insulation
- High temperature stability (up to ~1000°C in air)
- Chemically inert
- Lubricating ability (h-Boron Nitride)
- Extremely hard (c-BN, w-BN)
�� Common Uses
- Lubricants (especially high-temperature or dry lubricants)
- Thermal interface materials in electronics
- Electrical insulators
- Coatings for high-temperature equipment
- Cutting tools (c-BN)
- Crucibles for metal processing
- Cosmetic powders (soft, silky feel)

�� Safety Notes
- Generally considered non-toxic and safe
- Stable and inert
- Not known to cause environmental or health harm under normal use
�� General Characteristics Summary
| Property | Description |
| Chemical Formula | Boron Nitride (BN) |
| Appearance | White, soft powder (h-BN) |
| Stability | High thermal & chemical stability |
| Conductivity | High thermal, low electrical |
| Key Feature | Exists in forms similar to graphite & diamond |
