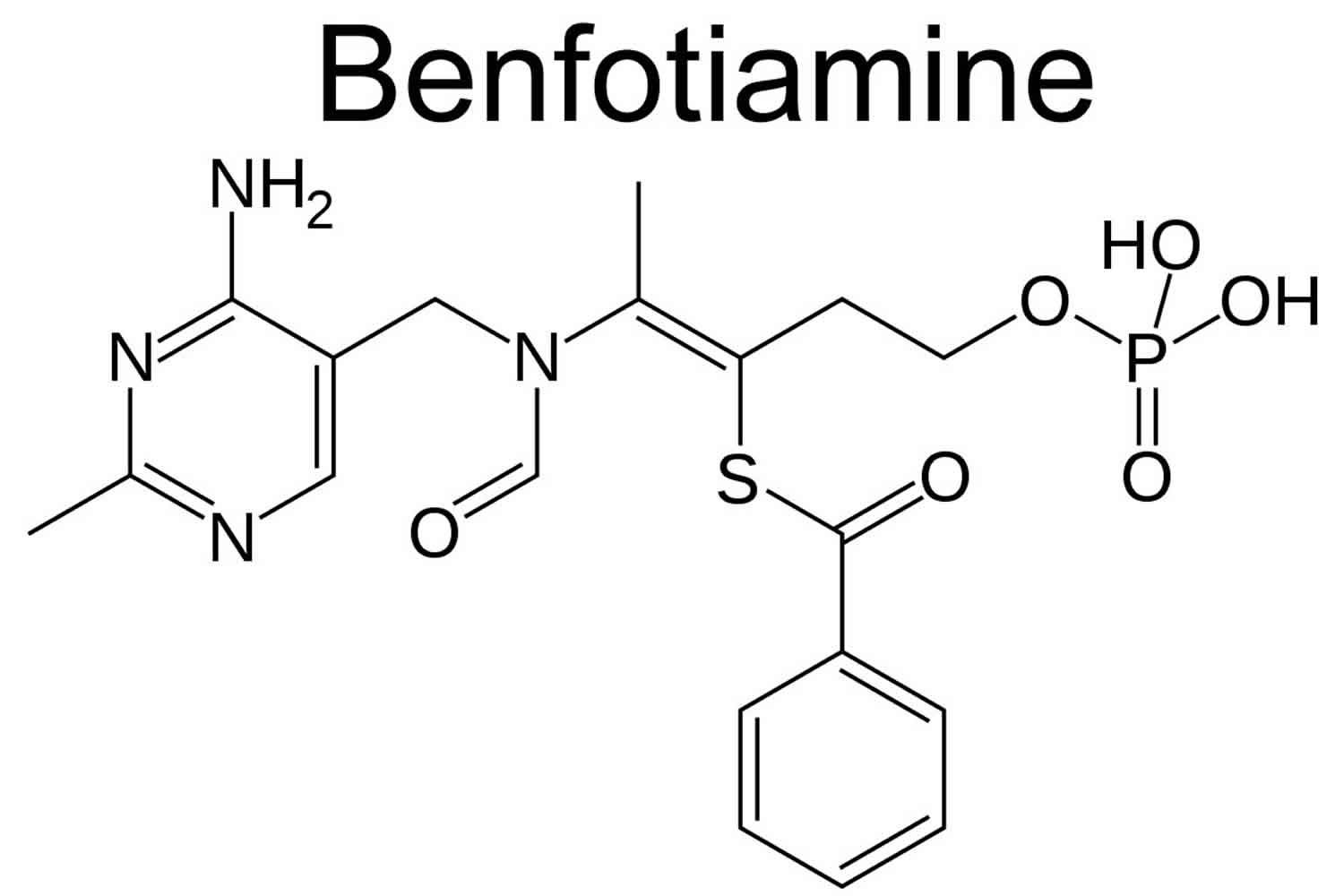
Benfotiamine is basically a synthetic fat-soluble derivative of vitamin B1 (thiamine).
To be more precise:
Parent / basic ingredient:
→ Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
Benfotiamine is chemically:
- S-benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate
So the core backbone is thiamine, but modified with a benzoate (benzoyl) group and a phosphate group to make it:
- more lipid soluble
- more stable in the intestine
- easier to absorb into cells
That is why benfotiamine is often called:
- a thiamine prodrug
- a bio-enhanced vitamin B1 source
Once inside the body → the body converts benfotiamine back into active thiamine coenzymes (mainly thiamine diphosphate) that participate in energy metabolism and anti-glycation pathways.

Adverse effects of Benfotiamine
Benfotiamine is generally one of the safer supplements in the B-vitamin family.
But adverse effects can still appear (esp. in higher doses, chronic use, or in sensitive people).
Most commonly reported
| Category | Details |
| GI upset | mild nausea, upset stomach, diarrhea (usually dose related) |
| Headache | usually from starting at high dose suddenly |
| Flushing / warmth | transient, similar to other B-complex reactions |
| Dizziness | rare, but reported anecdotally |
| Skin reactions | rare itching or mild rash, mainly in hypersensitive people |
Allergies / Hypersensitivity
Benfotiamine is a thiamine derivative → if someone has known true thiamine allergy (very rare) → potential cross-reactivity.
Also capsule excipients could cause reactions (gelatin, dyes, rice flour, magnesium stearate etc.)
Metabolic / Lab Interactions
Not many, but in high doses + long period:
- May slightly lower homocysteine but that’s not dangerous
- Theoretical interaction with diabetes drugs: blood glucose may be a bit lower so monitor if on hypoglycemics (this is not strong clinical evidence but caution is suggested)
Populations that should be careful
| Population | Why Caution |
| Pregnant / Breastfeeding | Insufficient robust human safety trials at supplemental high doses |
| Severe kidney disease | Theoretical accumulation (fat-soluble) |
| On multiple anti-diabetic meds | Watch glucose trend |
Serious adverse effects?
No well documented serious toxicity at normal supplemental doses (e.g. 150–600 mg/day).
Its LD50 is extremely high → basically not practically toxic at normal human doses.
Practical tips to minimize issues
- Start at 150 mg/day for 3–4 days → then go up
- Take with meal if stomach sensitive
- Avoid “complex blends” with many co-ingredients → makes it harder to know what caused reaction
If you want, I can also list the most evidence-based dose ranges depending on goal (neuropathy / anti-AGE / general metabolic support).
