Bacillus licheniformis is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, spore-forming bacterium commonly found in soil, water, and decomposing plant material. It is widely used in biotechnology and industrial applications due to its ability to produce enzymes and antibiotics. Here are its key characteristics:
General Characteristics:
- Scientific Classification: Belongs to the Bacillus genus within the Firmicutes phylum.
- Gram Staining: Gram-positive.
- Shape: Rod-shaped (bacillus).
- Motility: Motile due to peritrichous flagella.
- Spore Formation: Produces heat-resistant endospores, allowing survival in harsh conditions.
- Oxygen Requirement: Facultative anaerobe (can grow with or without oxygen).
- Colony Morphology: Forms rough, irregular colonies on agar plates.
Metabolic and Physiological Traits:
- Thermophilic: Can tolerate high temperatures (optimal growth around 50°C).
- Enzyme Production: Produces industrially significant enzymes such as proteases, amylases, lipases, and xylanases.
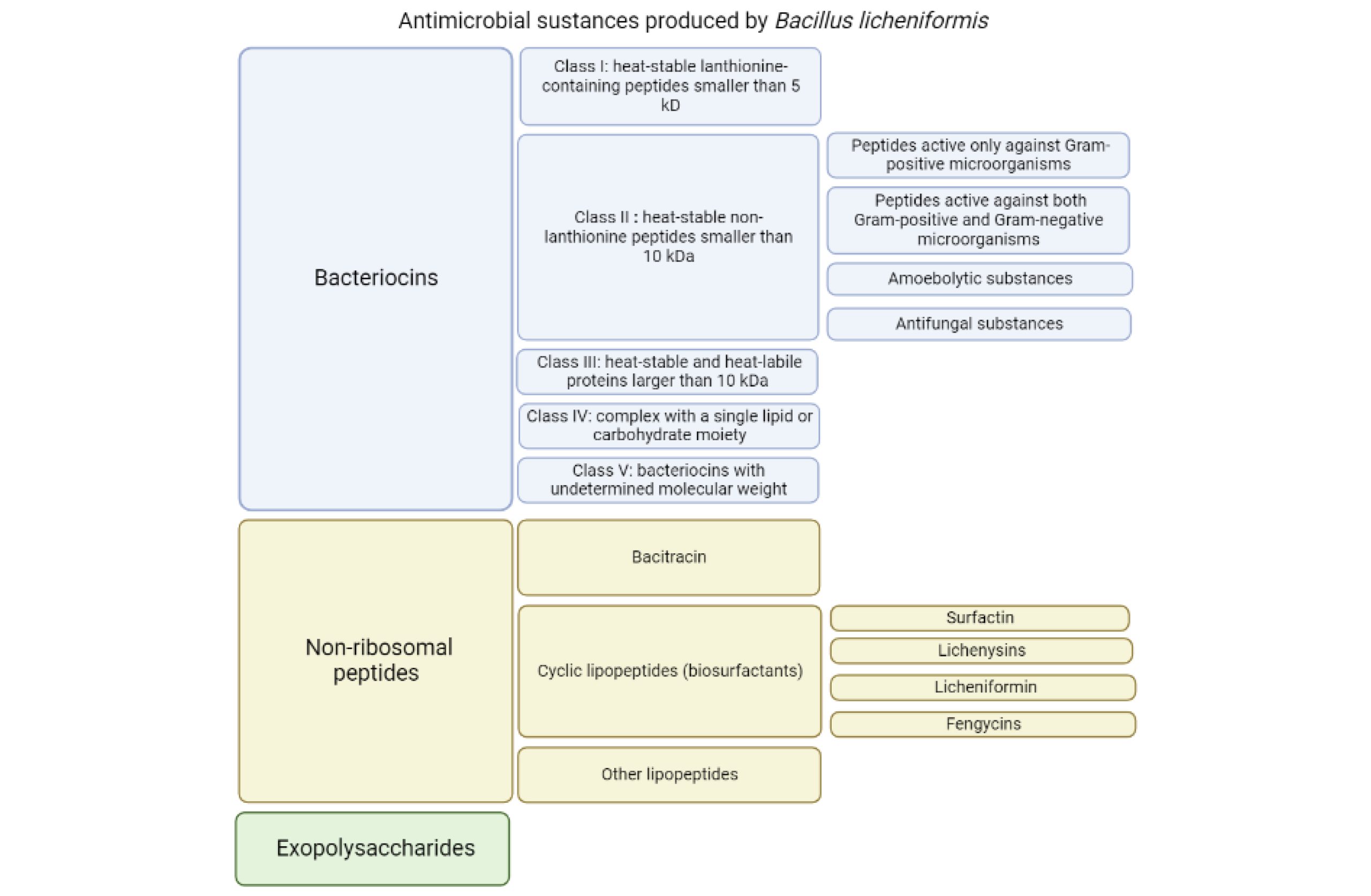
- Antibiotic Production: Produces bacitracin, a polypeptide antibiotic.
- Carbon Source Utilization: Can break down complex organic materials, aiding in nutrient cycling in soil.
Ecological and Industrial Importance:
- Bioremediation: Helps degrade pollutants and organic waste.
- Agricultural Use: Used as a biofertilizer and plant growth promoter.
- Probiotic Properties: Sometimes used in animal feed for gut health.
- Food and Biotechnology: Produces enzymes for detergents, textile processing, and food industry applications.
Would you like details on a specific aspect of Bacillus licheniformis?
