D-Chiro-Inositol (DCI) is a stereoisomer of inositol, which is a cyclohexanehexol (six-carbon cyclic polyol with six hydroxyl groups).
Chemical Structure
1. Chemical formula: C₆H₁₂O₆
2. Molecular weight: 180.16 g/mol
3. IUPAC name: (1R,2S,3R,4S,5S,6S)-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol
4. Stereochemistry: It has six chiral centers; the “D-Chiro” configuration refers to the specific orientation of hydroxyl (-OH) groups on the cyclohexane ring.
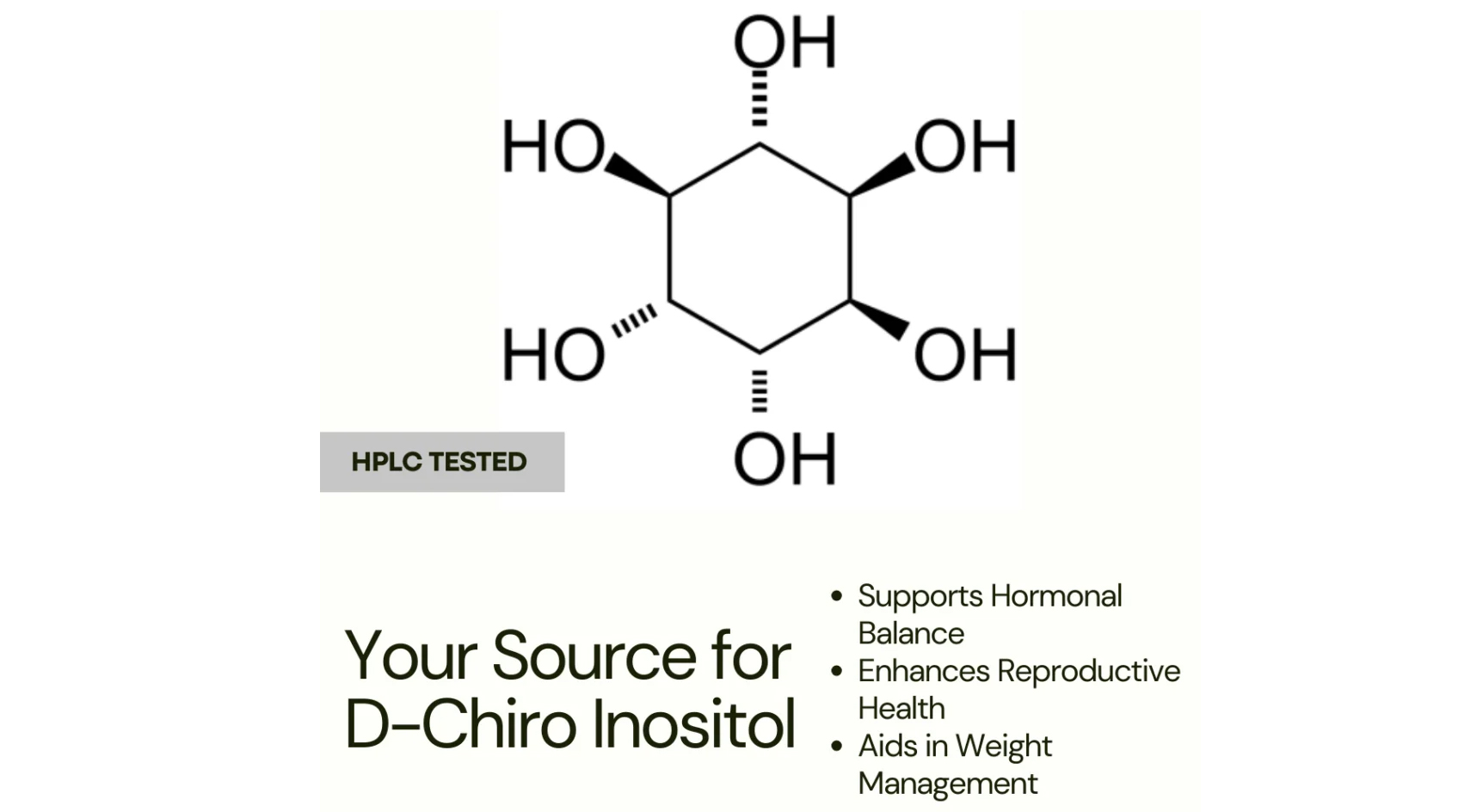
5. Structural features:
Cyclohexane ring (chair conformation is most stable)
Hydroxyl groups arranged in a specific “chiro” pattern:
- At carbons 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6: OH groups alternate between axial and equatorial positions, giving D-Chiro-Inositol distinct biological activity compared to other inositol stereoisomers.
You can visualize it as a six-membered ring with hydroxyls oriented differently from myo-inositol, its most common stereoisomer.
Physical Properties
| Property | Value / Description |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol |
| Melting Point | ~226–230 °C (decomposes) |
| Taste | Sweet |
| Optical Rotation | [α]D ≈ +15° to +20° (varies slightly by source and purity) |
| Hygroscopicity | Slightly hygroscopic; can absorb moisture from air |
| Stability | Stable under normal temperature; sensitive to strong acids and bases |
Key Notes
- D-Chiro-Inositol is non-toxic and naturally occurring in foods such as legumes, buckwheat, and carob.
- Its water solubility makes it suitable for supplements and pharmaceutical formulations.
- Unlike myo-inositol, D-Chiro-Inositol plays a critical role in insulin signaling, acting as a secondary messenger for glucose uptake.
