Chemical Structure
Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol is a derivative of chromanol, which is a bicyclic structure combining a chromane ring (a benzopyran) with a hydroxyl group. Its full chemical name is often given as 2,2,5,7,8-pentamethyl-6-chromanol or related variants depending on methylation positions.
Core structure: Chromanol (chromane with a hydroxyl group at position 6 or 7)
Functional groups:
- Hydroxyl (-OH): Acts as an antioxidant site.
- Methoxy (-OCH₃) group: Increases lipophilicity.
- Dimethyl substitutions: Often on the chromanol ring, enhancing stability and radical-scavenging activity.
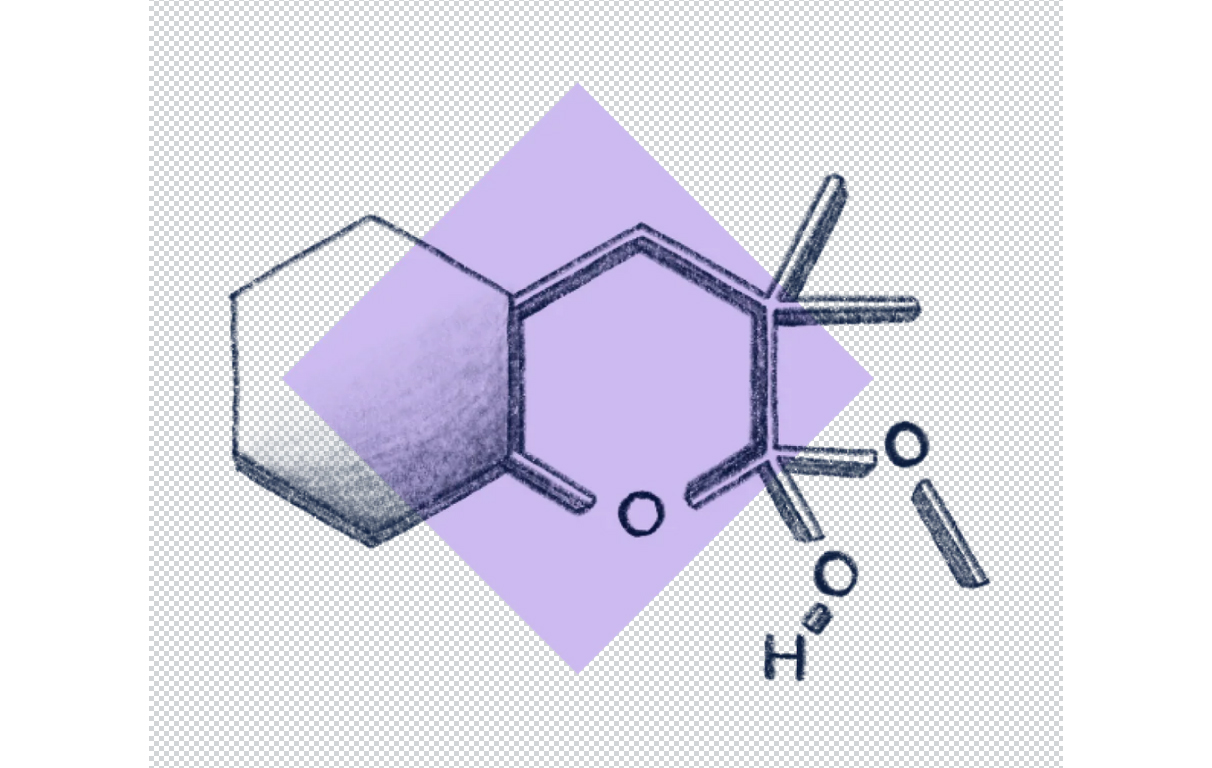
Molecular formula (approximate): C₁₄H₂₂O₂
Molecular weight: ~222 g/mol
Physical Properties
| Property | Value / Description |
| Appearance | Off-white to pale yellow crystalline solid |
| Solubility | Lipophilic; soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, oils; poorly soluble in water |
| Melting point | ~50–60 °C (depends on purity) |
| Stability | Stable under normal conditions; sensitive to strong oxidizing agents and high heat |
| LogP (partition coefficient) | ~6–7 (highly lipophilic, can cross lipid membranes) |
| UV Absorption | Strong absorption in 290–330 nm (due to chromanol ring) |

Key Notes
- The hydroxyl group makes it a strong free radical scavenger, particularly for ROS (reactive oxygen species) in biological systems.
- The dimethyl and methoxy substitutions improve lipid solubility and bioavailability, making it useful in skincare formulations and supplements.
- It is chemically stable under normal storage but can degrade in strongly acidic/basic conditions or upon prolonged UV exposure.
If you want, I can also draw a precise 2D chemical structure of Dimethylmethoxy Chromanol for better visualization—it’s especially useful if you need it for papers or presentations.
