L-Arginine is an amino acid with the chemical formula C6H14N4O2. It is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. L-Arginine is classified as a semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that under normal circumstances, the human body can synthesize it, but there are certain conditions where dietary intake becomes essential.
Here is the chemical structure of L-Arginine:
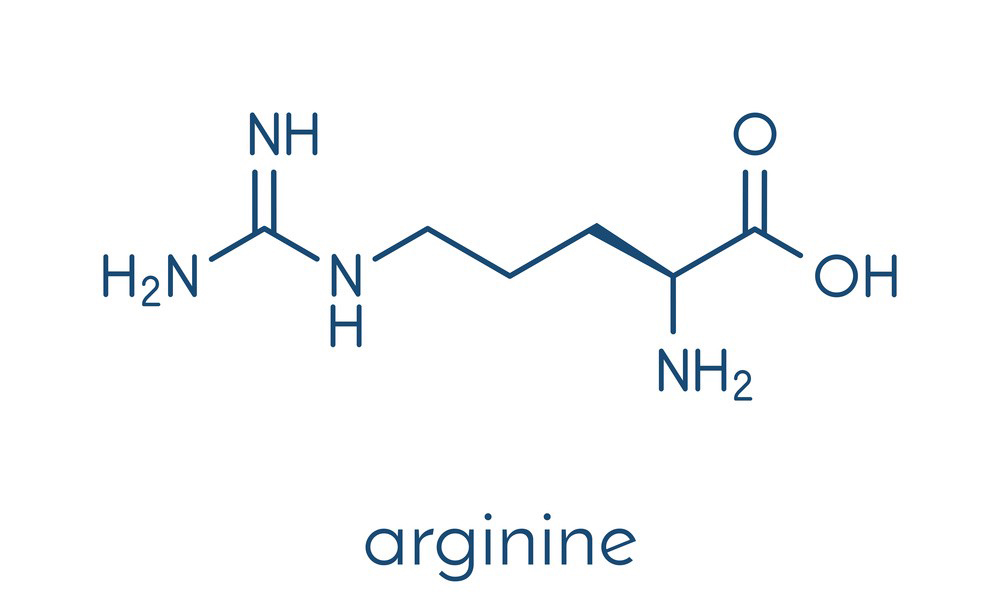
L-Arginine contains a guanidinium group, which gives it unique properties compared to other amino acids. Some of the physical properties and characteristics of L-Arginine include:
1.Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of L-Arginine is approximately 174.2 grams per mole.
2.Solubility: L-Arginine is highly soluble in water, which is typical for amino acids. This property makes it easy for the body to transport and use in various biochemical reactions.
3.Melting Point: L-Arginine melts at a relatively high temperature, around 220-225 degrees Celsius (428-437 degrees Fahrenheit).
4.Taste: L-Arginine has a slightly bitter taste.
5.pKa Values: L-Arginine has three ionizable groups with corresponding pKa values: the carboxyl group (pKa1 ≈ 2.2), the alpha amino group (pKa2 ≈ 9.0), and the guanidinium group (pKa3 ≈ 12.5). These pKa values determine the ionization state of L-Arginine at different pH levels, making it important in various biochemical reactions.
6.Biological Functions: L-Arginine plays a crucial role in various biological processes. It serves as a precursor for the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that helps regulate blood vessel dilation and plays a role in cardiovascular health. L-Arginine is also involved in the urea cycle, which is responsible for removing ammonia from the body. Additionally, it is important for protein synthesis and wound healing.
7.Dietary Sources: L-Arginine can be obtained from dietary sources such as meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, nuts, and soybeans. It is also available as a dietary supplement.
It’s important to note that L-Arginine is used in various dietary supplements and is sometimes promoted for its potential health benefits, such as improving blood flow and athletic performance. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using any dietary supplements, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking medications, as excessive intake of L-Arginine can have side effects.
