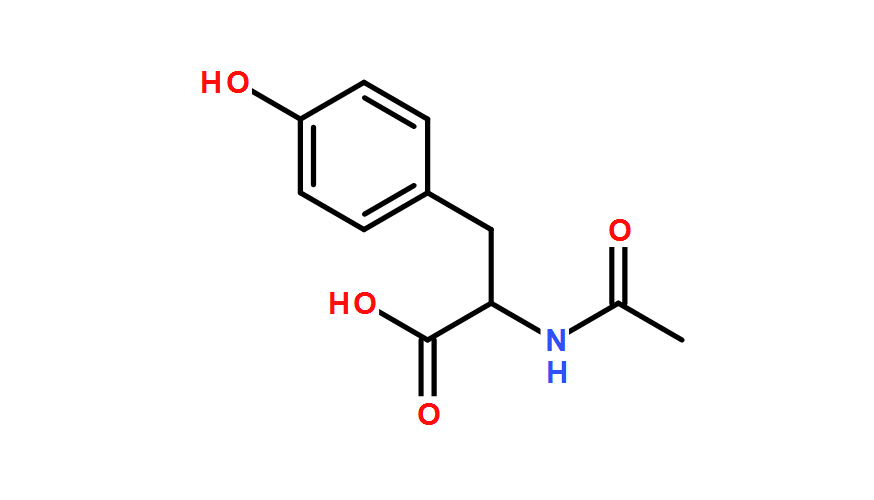
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine (NALT) is a modified form of the amino acid L-tyrosine, where an acetyl group (-COCH3) is attached to the nitrogen atom of the tyrosine molecule. Here’s a brief overview of its chemical structure and physical properties:
Chemical Structure:
- Chemical Formula: C11H13NO4
- Structure: N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine consists of a tyrosine molecule (an aromatic amino acid) with an additional acetyl group attached to the amino group (-NH2).
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Typically white to off-white crystalline powder.
- Solubility: N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is soluble in water and organic solvents like ethanol and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Melting Point: The exact melting point can vary slightly depending on the purity, but it generally melts around 140-145°C.
Chemical Properties:
- Stability: It is stable under normal conditions of use and storage.
- Acidity/Basicity: As a derivative of tyrosine, it can behave as a weak base or a weak acid depending on the pH of the solution.

Uses:
- Nutritional Supplement: N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is commonly used as a supplement due to its potential to enhance tyrosine availability in the body, which is a precursor for neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Some studies suggest that N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine may improve cognitive function and reduce stress, although more research is needed to confirm these effects.
In summary, N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is a modified amino acid derivative that retains the basic properties of L-tyrosine while offering improved solubility and potentially enhanced bioavailability. It is used primarily in supplements aimed at cognitive enhancement and stress reduction.
