Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in antioxidant defense mechanisms in cells. There are different forms of Superoxide dismutase, and the most common ones include copper-zinc SOD (Cu-Zn SOD), manganese SOD (Mn SOD), and iron SOD (Fe SOD). Here’s a brief overview of the chemical structure and physical properties of Cu-Zn SOD, which is the most well-known form:
Chemical Structure of Superoxide Dismutase:
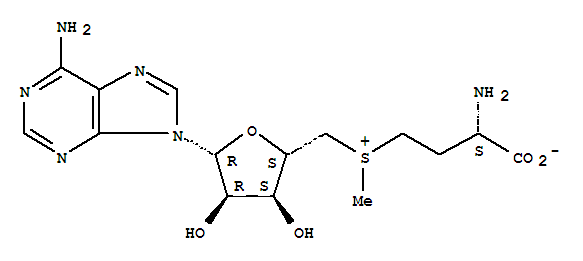
Cu-Zn SOD is a metalloenzyme, meaning it contains metal ions in its structure. The structure of Cu-Zn SOD includes two metal ions: copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn). The enzyme is a homodimer, meaning it consists of two identical subunits.
Each subunit contains one copper ion and one zinc ion, which are essential for the enzyme’s activity.
The copper ion is typically coordinated by four histidine residues, while the zinc ion is coordinated by three histidine residues and one aspartic acid residue.
The overall structure of Cu-Zn SOD is globular, and it forms a well-defined active site where the catalytic reactions take place.
Physical Properties of Superoxide Dismutase:
1.Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of Cu-Zn SOD is around 32 kDa for the dimeric form.
2.pI (Isoelectric Point): The isoelectric point is around pH 5.2 for Cu-Zn SOD.
3.Stability: Superoxide dismutase enzymes are generally stable proteins. Cu-Zn SOD, in particular, is stable under physiological conditions.
4.Cofactors: As mentioned, Cu-Zn SOD requires copper and zinc ions as cofactors for its catalytic activity.
5.Function: The primary function of Cu-Zn SOD is to catalyze the dismutation of superoxide radicals (O2-) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), thus preventing the formation of highly reactive and damaging reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells.
6.Localization: Cu-Zn SOD is found in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and extracellular spaces of cells.
Understanding the chemical structure and physical properties of superoxide dismutase provides insights into its biological function and its role in cellular defense against oxidative stress.
The application of Superoxide Dismutase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS are highly reactive molecules produced during normal cellular processes and can cause oxidative stress, leading to cell damage and aging. Superoxide dismutase catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide radicals into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, thereby reducing the harmful effects of ROS.

Here are some applications of Superoxide Dismutase:
Antioxidant Therapy: Superoxide dismutase is often used in antioxidant therapy to neutralize excess free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. This has potential applications in various medical conditions associated with oxidative damage, such as neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory disorders.
Skin Care: Due to its antioxidant properties, Superoxide dismutase is incorporated into skincare products to protect the skin from oxidative stress and premature aging. It helps in maintaining skin health and reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Superoxide dismutase has anti-inflammatory properties and can be used to modulate inflammatory responses. This makes it a potential therapeutic agent for conditions characterized by chronic inflammation.
Radioprotection: Superoxide dismutase has been explored for its radioprotective effects. It may help protect cells from damage induced by ionizing radiation, making it a potential candidate for use in cancer treatment to minimize side effects on healthy tissues.
Neuroprotection: Superoxide dismutase has shown promise in protecting neurons from oxidative stress, making it a potential therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Sports Medicine: Superoxide dismutase may be used in sports medicine to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation associated with intense physical activity. It could aid in recovery and reduce muscle damage.
Biotechnology: Superoxide dismutase is used in biotechnology processes to protect cells and tissues from oxidative damage during various procedures, such as cell culture and bioprocessing.
It’s important to note that while Superoxide dismutase has therapeutic potential, its applications are still under research in many areas, and more studies are needed to fully understand its efficacy and safety in different contexts. As with any therapeutic agent, caution should be exercised, and professional medical advice should be sought before using Superoxide dismutase for specific medical conditions.
