Introduction of Boron Nitride (BN)
Boron Nitride (BN) is an inorganic compound composed of boron (B) and nitrogen (N), typically with a 1:1 atomic ratio. It is often compared to carbon because BN can form several structural polymorphs that resemble forms of carbon:
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) → similar to graphite
- Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN) → similar to diamond
- Wurtzite Boron Nitride (w-BN) → similar to lonsdaleite
Boron Nitride is widely used in electronics, ceramics, lubrication, cosmetics, high-temperature systems, and nanomaterials.
Origin of Boron Nitride
Natural Origin
- Boron Nitride is extremely rare in nature.
- A natural mineral called boron nitride (boron-nitrogen compound) is sometimes found in volcanic and metamorphic rocks but in trace amounts.
- Most Boron Nitride used commercially is synthetic.
Synthetic Origin
Boron Nitride production began in the 20th century during research on refractory materials and superhard materials. Key developments:
- Early 1900s: First synthesized in laboratories.
- 1950s–1960s: Development of cubic BN (c-BN) by General Electric using high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) technologies — similar to synthetic diamond production.
- Modern era: Low-pressure methods, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and solution synthesis expanded uses in electronics and nanotechnology.
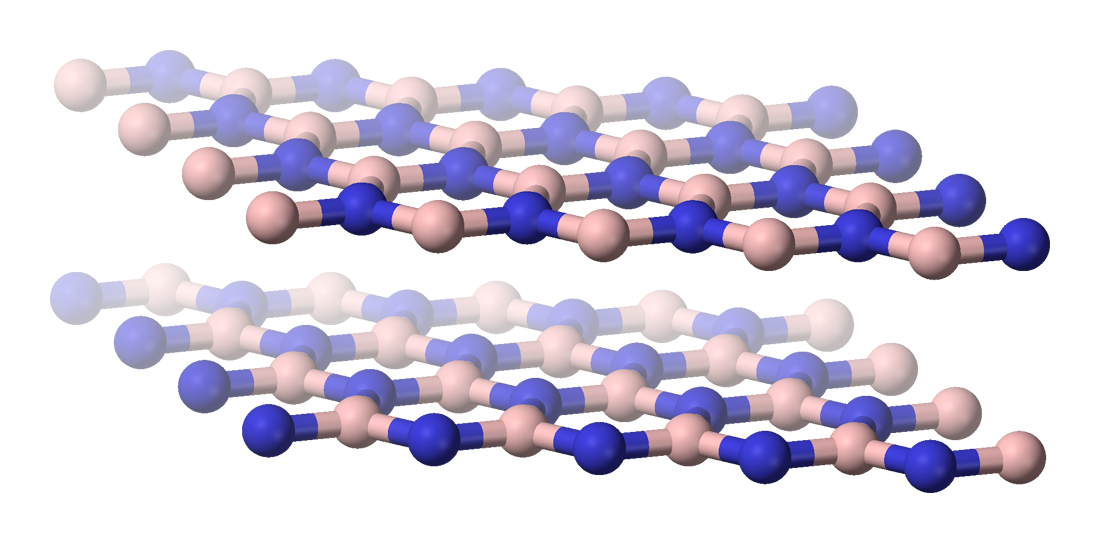
Chemical Structure of Boron Nitride
Boron Nitride consists of alternating B and N atoms.
The bonding is strongly covalent but has partial ionic character because N is more electronegative than B.
Common Boron Nitride polymorphs
| Form | Structure | Carbon Analogue | Key Features |
| h-BN | layered, hexagonal | graphite | lubricating, insulating, thermally conductive |
| c-BN | cubic, zinc-blende | diamond | extremely hard, chemically stable |
| w-BN | wurtzite | lonsdaleite | superhard (rare) |
| a-BN | amorphous | amorphous carbon | precursor for crystalline Boron Nitride |
Physical and Chemical Properties of Boron Nitride
A. Physical Properties
1. Color: white, opaque or translucent
2. Density:
- h-BN: ~2.1 g/cm³
- c-BN: ~3.45 g/cm³
3. Melting Point: ~2973 °C (sublimes before melting)
4. Thermal Conductivity:
- high along h-BN layers (~600 W/m·K)
5. Electrical Properties:
- excellent electrical insulator
- bandgap: 5.5–6.0 eV
6. Hardness:
- c-BN: second only to diamond
- w-BN: potentially harder than diamond (rare)
B. Chemical Properties
- Chemically stable and inert
- Resistant to oxidation (up to ~900 °C in air)
- Stable in many acids and molten metals
- Not wet by most metals (good for foundry applications)

Key Characteristics
- High thermal conductivity but electrically insulating
- Excellent lubricating properties (h-BN)
- Strong resistance to corrosion
- Lightweight and thermally stable
- Refractory (high-temperature stability)
Summary
Boron Nitride is a versatile advanced material, notable for its carbon-like polymorphs, exceptional thermal properties, chemical stability, and wide industrial applications. Whether in electronics, lubrication, coatings, or cutting tools, Boron Nitride plays a crucial role due to its unique combination of mechanical, thermal, and electrical features.
