Benfotiamine is a synthetic derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1) that is more lipid-soluble, which allows it to be better absorbed and penetrate tissues more effectively than regular thiamine. Its pharmacological effects are mainly related to glucose metabolism, nerve function, and protection against complications of diabetes. Here’s a detailed overview:
1. Enhancement of Thiamine Levels
- Benfotiamine is converted into thiamine in the body.
- It increases thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), the active coenzyme form of vitamin B1.
- TPP is essential for carbohydrate metabolism, particularly in the pentose phosphate pathway and Krebs cycle.
2. Improvement of Glucose Metabolism
- Activates the transketolase enzyme, which shunts excess glycolytic intermediates into the pentose phosphate pathway.
- Helps reduce the formation of harmful advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- Reduces hyperglycemia-induced cellular damage, especially in vascular and nerve tissues.

3. Neuroprotective Effects
- Supports peripheral nerve function, reducing symptoms like numbness, tingling, and pain in diabetic neuropathy.
- Protects neurons from oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
- May enhance nerve conduction velocity.
4. Vascular Protective Effects
- Inhibits AGE accumulation in blood vessels.
- Reduces endothelial dysfunction, which can lower the risk of microvascular complications in diabetes.
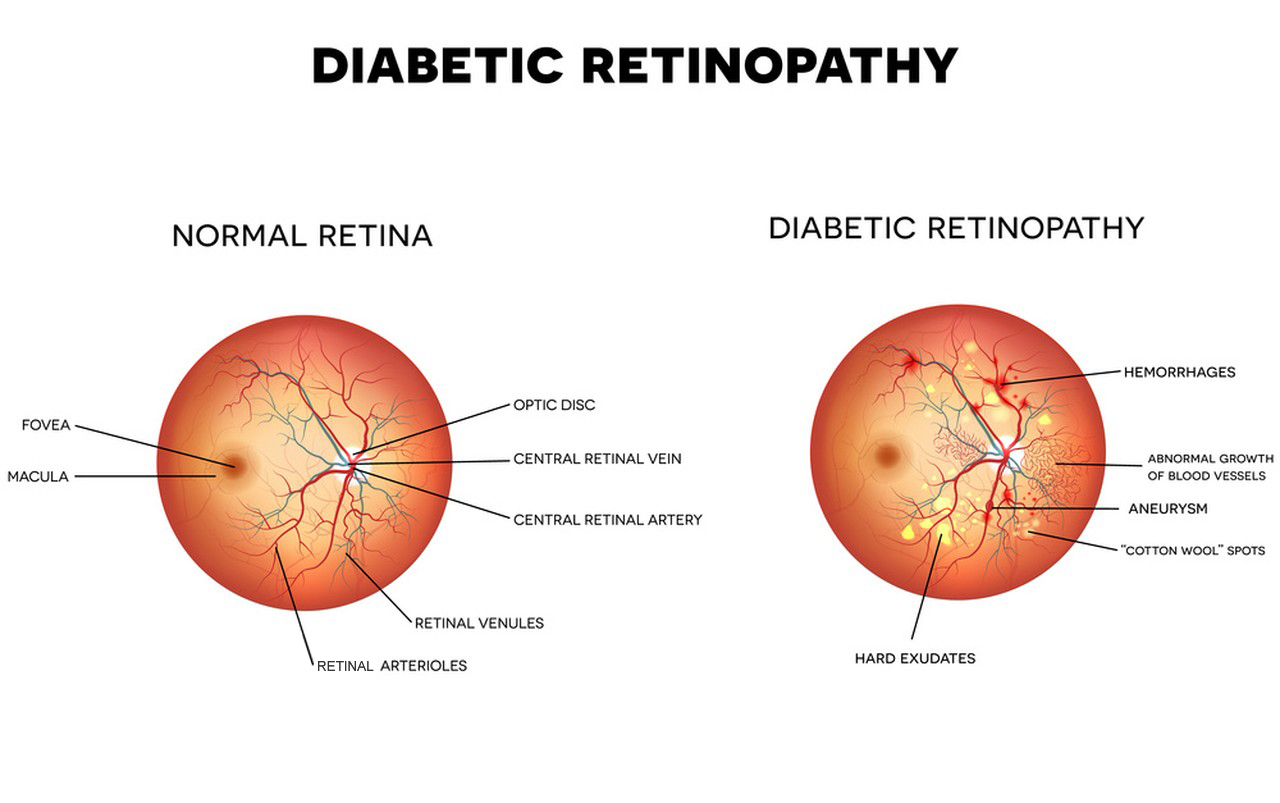
- Helps prevent diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and atherosclerosis in experimental studies.
5. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
- Reduces oxidative stress markers.
- Suppresses pro-inflammatory pathways, particularly those triggered by high glucose.
- Protects against tissue damage in kidneys, nerves, and eyes.
6. Potential Cognitive Benefits
- Some studies suggest it may improve cognitive function in early Alzheimer’s disease or prevent cognitive decline in diabetic patients.
- Mechanism: reduction of glucose toxicity in neurons, decreased AGE accumulation, and oxidative stress reduction.
Summary
Benfotiamine pharmacologically acts as a potent thiamine supplement with enhanced bioavailability, primarily targeting:
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Diabetic complications (neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy)
- Oxidative stress and inflammation
- Vascular and neural protection
If you want, I can also make a diagram showing Benfotiamine’s mechanisms in the body, which makes it much easier to visualize its effects. Do you want me to do that?
