Bacillus Thuringiensis
Bacillus Thuringiensis Israelensis, abbreviated as Bt, also known as Bacillus thuringiensis, is a type of crystal-forming Bacillus that includes many varieties. The bacteria can produce two major toxoids, namely endotoxin (with crystals) and exotoxin. After the pests are fed, the bacteria release toxins, poison the bacteria and stop feeding, and finally the pests under the action of the alkaline digestive juice of the intestines. Death due to hunger and blood and nerve poisoning. Therefore, the bacterium can be used as a microbial low-toxic insecticide for controlling a variety of pests of Orthoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, Hymenoptera, especially Lepidoptera.
Description

| Product name | Bacillus Thuringiensis Israelensis |
| Other name: | Bactospeine; Bt; BACILLUS THURINGENSIS; BIOTROL4K; Bacilex; THURICIDE-HP; DIPEL |
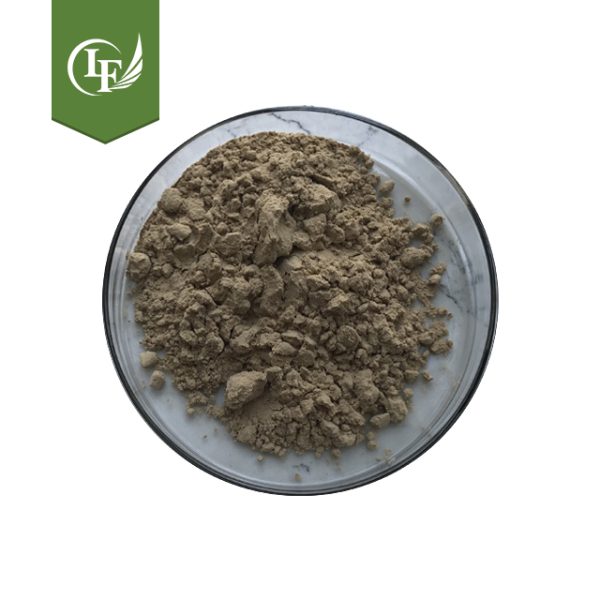
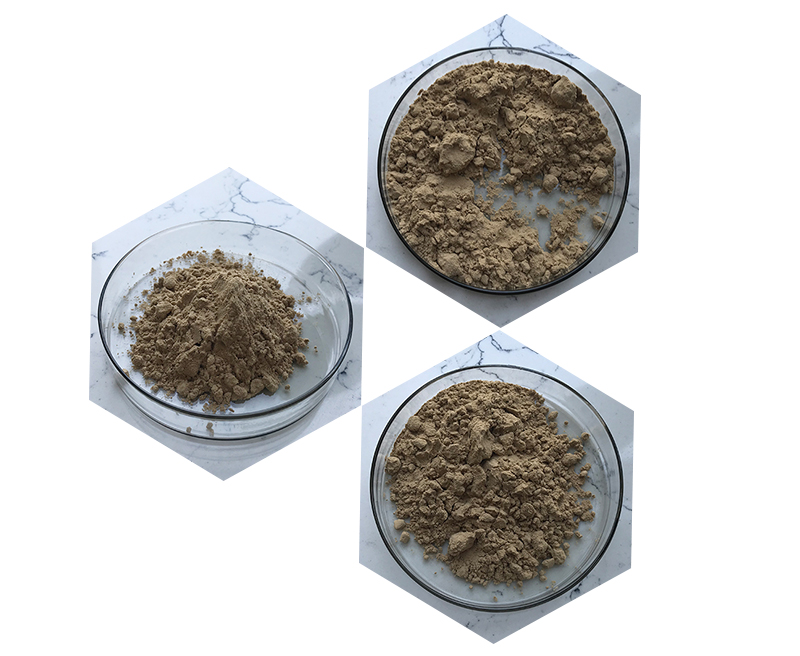
| Appearance | Brown powder or light brown powder, odorless |
| Sample | Available |
| Storage | Cool Dry Place |

Bacillus thuringiensis has different pathogenic and toxic effects on more than 100 insect pests, such as cotton bollworm, Chinese cabbage insect, poisonous moth, pine caterpillar, corn borer, sorghum borer, etc.
Mechanism of action when the insect nibbleth the spore crystals and spores, the spore crystals dissolve in the intestinal alkaline environment of the insect, releasing the toxin which has a strong killing effect on Lepidoptera larvae.
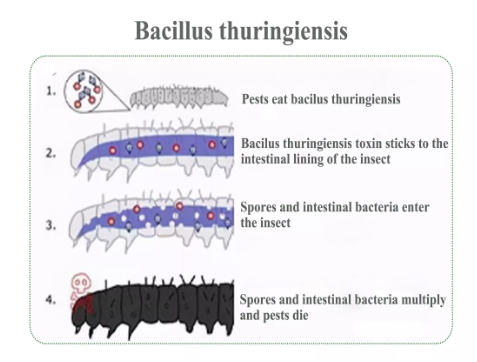
This toxin causes the midgut paralysis of the larvae, showing poisoning symptoms, and generally does no harm to the crops. After a period of onset, the intestinal wall of the insect is damaged, the toxin enters the blood,causing septicemia, and at the same time the spores multiply rapidly in the digestive tract, accelerating the death of the insect.
Bacillus Thuringiensis Advantage:
1. Strong selectivity and no harm to natural enemies
2.Not affect the activities of soil microorganisms
3.No residual poison, the production of products can be safe to eat




- More Than 10 Years Experience in the Field of Health and Export (Established in 2011,And Developed 3 Branch Companies)
- Certificate Of ISO, Halal And Kosher
- High Standard Workshop And Visitors Welcome At Any Time
- Professional Team
- Providing OEM Service
- Transaction Guarantee And Convenient Payment Terms Available
- Professional Packing And Custom Packing Service
- Providing Visual Delivery Process
- Providing Refunds Or Exchanges Servic

We Provide You The Sincerest And Most Professional Service As Follow:
1. Sales
- 24 Hours of Market Information
- Sharing of Market Information Trend
- Suggestion for Purchase Decision
2. Payment
- Different Payment Terms:TT,LC And So On
- Multiple Payment Methods:Bank Transfer, Credit Card, Paypal Etc.
- Funds Risk Control
3. Shipment Conditions
- Fast Shipping Within 3 Working Days Usually
- Update for Full Shipment Process From China to Destination
- Cooperation for Fast&Smooth Custom Clearance at Destination
4. Reputation
- Implementing Contract Terms Strictly
- Timely Solving Any Discrepancy or Goods Claims
- Responsible for Loss Under Our Liability Others
5. Others
- Assistant: Sample Working; Help You Solve The Problem in China
- Registration : Professional Team for Registration in Market
- Technology: Rich Experienced Technician to Support













