Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) is a chelating agent that has been used clinically for various purposes, primarily in the field of nephrology, radiology, and toxicology.
Applications of DMSA
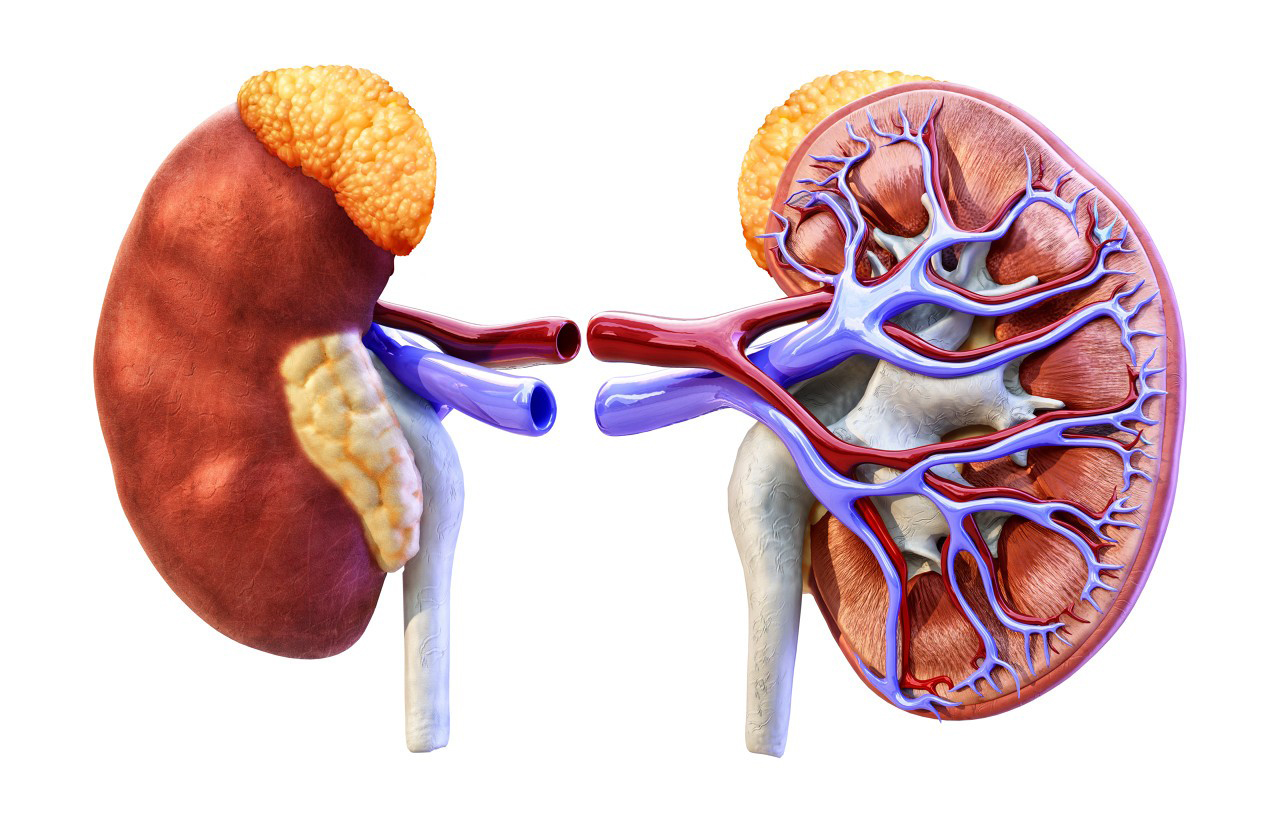
Renal Imaging (Scintigraphy): DMSA is commonly used in nuclear medicine for renal imaging. It is injected into a patient’s bloodstream and taken up by the kidneys, where it binds to renal cortical tissue. This allows for the visualization and assessment of the kidney’s structure and function using gamma camera imaging. DMSA renal scintigraphy is used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as renal scarring, infection, and vesicoureteral reflux.
Assessment of Kidney Function: DMSA renal scintigraphy can also be used to assess the overall function of the kidneys, particularly the individual function of each kidney. This can be important in cases of kidney disease or when evaluating potential kidney donors.
Heavy Metal Poisoning: DMSA has been used in cases of heavy metal poisoning, especially for lead poisoning. It acts as a chelating agent, meaning it can bind to heavy metals and help facilitate their excretion from the body, reducing their toxic effects. DMSA can be administered orally to treat lead poisoning, especially in children.
Mercury Poisoning: DMSA has also been investigated for its potential use in treating mercury poisoning. It can bind to mercury and aid in its elimination from the body, although its effectiveness can vary depending on the type of mercury exposure.
Chelation Therapy: DMSA is sometimes used in chelation therapy for individuals with suspected heavy metal toxicity. It may be used in combination with other chelating agents and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Research: DMSA has been utilized in research settings to study kidney function, heavy metal toxicity, and other related areas. Its chelating properties make it valuable for understanding the mechanisms of heavy metal interactions in the body.
It’s important to note that DMSA should be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional, as improper use or dosing can lead to adverse effects. Additionally, the clinical use of DMSA may have evolved since my last update in September 2021, so it’s a good idea to consult the latest medical literature or medical professionals for the most current information on its clinical applications.
Adverse effects of DMSA
Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) is a chelating agent that is commonly used in medical settings to treat heavy metal poisoning, particularly lead poisoning. It works by binding to heavy metals in the body and aiding their excretion through urine. While DMSA is generally considered safe and effective when used under medical supervision, like any medication, it can have potential adverse effects. Some possible adverse effects of DMSA include:
Gastrointestinal Distress: DMSA can cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. These effects are usually mild and transient.
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to DMSA, which can manifest as skin rashes, itching, or swelling. In severe cases, anaphylactic reactions (a serious allergic response) could occur, although these are extremely rare.
Elevated Liver Enzymes: In some cases, DMSA treatment might lead to a temporary increase in liver enzyme levels. This usually resolves once the treatment is discontinued.
Hematological Effects: DMSA can affect blood cell counts, leading to changes in white blood cell, red blood cell, or platelet counts. However, these effects are typically reversible upon discontinuation of the treatment.
Kidney Function Changes: DMSA primarily excretes heavy metals through the kidneys. In rare cases, it might affect kidney function, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney issues. Regular monitoring of kidney function is important during DMSA treatment.
Neurological Symptoms: There have been reports of neurological symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and confusion during DMSA treatment, but these are relatively uncommon.
Metal Imbalance: While DMSA is intended to remove toxic heavy metals, it can also bind to essential minerals like zinc and copper. This might lead to temporary imbalances in these essential metals, potentially causing deficiency-related symptoms.
Bone Marrow Suppression: There have been rare cases where DMSA treatment was associated with bone marrow suppression, which can lead to decreased production of blood cells. This can result in anemia, lowered immunity, and other blood-related issues.
Interactions with Other Medications: DMSA might interact with other medications that a person is taking, potentially affecting their effectiveness or causing adverse reactions. Therefore, it’s important to inform healthcare providers about all medications being used.
It’s important to note that the occurrence of these adverse effects is generally rare and often outweighed by the benefits of treating heavy metal poisoning. DMSA should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional who can monitor for potential adverse effects and adjust the treatment plan accordingly. If you or someone you know is considering DMSA treatment, it’s best to consult a medical doctor to assess the potential risks and benefits based on the individual’s specific health condition.
