Boron Nitride (BN) is a versatile compound with many important industrial, scientific, and technological uses due to its unique combination of high thermal stability, electrical insulation, and chemical inertness. Its applications vary depending on its crystal form—mainly Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN), Cubic Boron Nitride(c-BN), and Amorphous Boron Nitride (a-BN).
1. Industrial and Engineering Uses
a. Lubricants and Coatings
Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) acts like graphite — it’s a solid lubricant effective at high temperatures (up to 900 °C in air).
Used as coatings on molds, dies, and furnace components to reduce friction and wear.
b. High-Temperature Equipment
Because Boron Nitride resists oxidation and thermal shock, it’s used in:
- Crucibles, boats, and tubes for metal and glass melting.
- Protective coatings in vacuum and plasma environments.
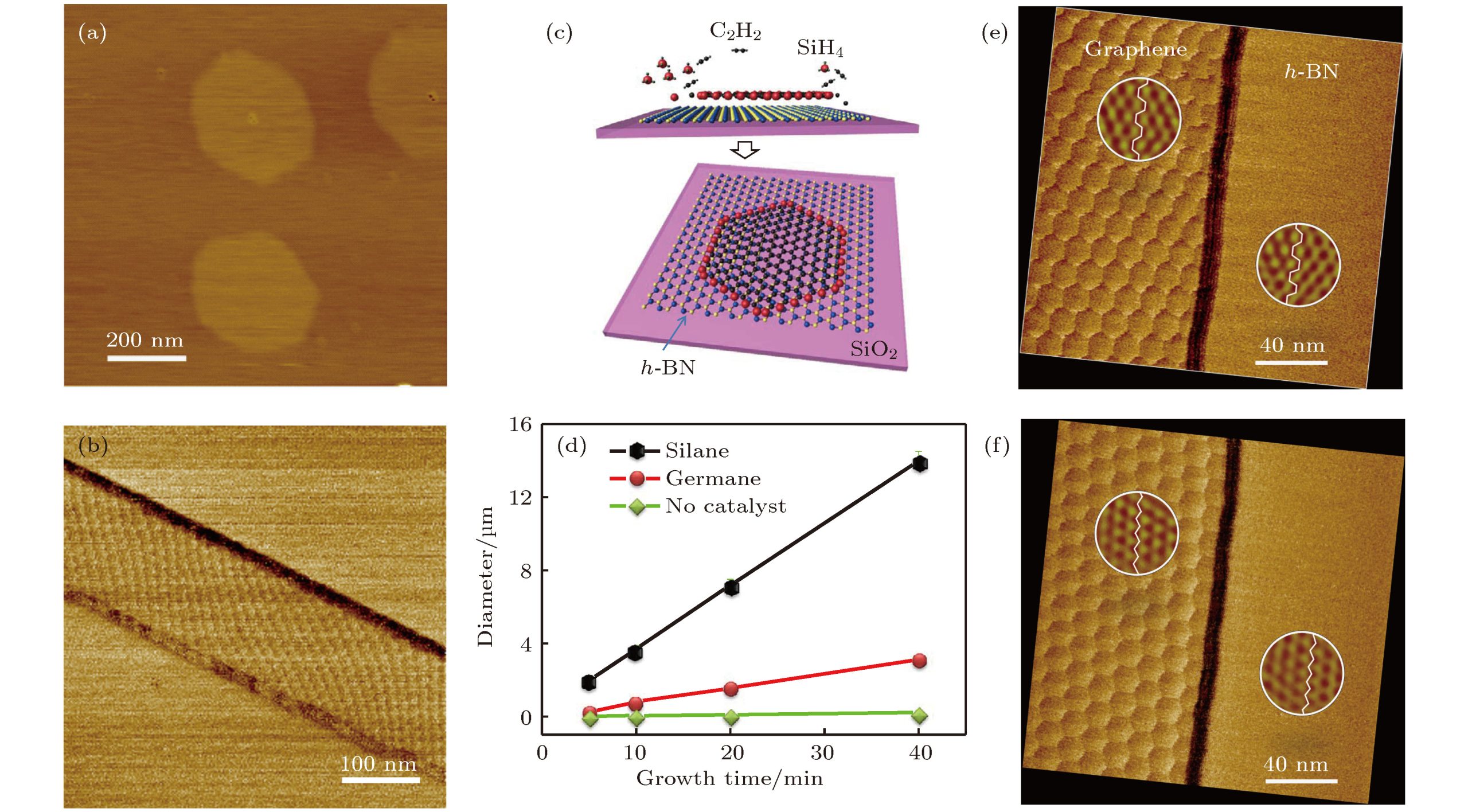
2. Electronic and Electrical Applications
a. Electrical Insulator
Boron Nitride is an excellent electrical insulator but has high thermal conductivity, making it ideal for:
- Heat sinks in electronic devices.
- Substrates and insulating layers in semiconductors and LEDs.
b. Dielectric Layers
Used in 2D electronics, especially with graphene, as a dielectric and barrier layer—helping stabilize electronic performance.
3. Cutting and Abrasive Materials
Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN) is the second hardest material after diamond.
Commonly used for:
- Cutting tools and abrasives for hard steels and superalloys.
- Grinding wheels and machining tools that require high hardness and thermal resistance.
4. Thermal Management
Boron Nitride composites and ceramics efficiently dissipate heat without conducting electricity.
Used in:
- Thermal interface materials in electronics.
- Heat spreaders in power devices and batteries.
5. Cosmetics and Personal Care
Fine Boron Nitride powder provides:
- Silky texture and oil absorption in cosmetics.
- Used in foundations, eyeshadows, and powders to improve smoothness and brightness.
6. Composite and Structural Materials
Added to polymers, ceramics, and metals to enhance:
- Thermal conductivity
- Lubrication
- Wear and oxidation resistance
7. Research and Advanced Applications
In nanotechnology, Boron Nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) show promise for:
- Reinforced composites
- Radiation shielding
- Hydrogen storage
8. Medical and Biotechnological Uses
Boron Nitride is biocompatibility makes it suitable for:
- Drug delivery systems
- Biomedical implants
- Protective coatings for medical devices
Summary Table
| Form | Main Properties | Typical Uses |
| Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) | Lubricant, thermally stable, electrically insulating | Coatings, lubricants, insulators, cosmetics |
| Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN) | Superhard, chemically stable | Cutting tools, abrasives |
| Amorphous Boron Nitride (a-BN) | Amorphous, dielectric | Thin films, coatings, insulators |
Would you like me to make an illustrated chart summarizing these applications by industry (electronics, cosmetics, aerospace, etc.)?
