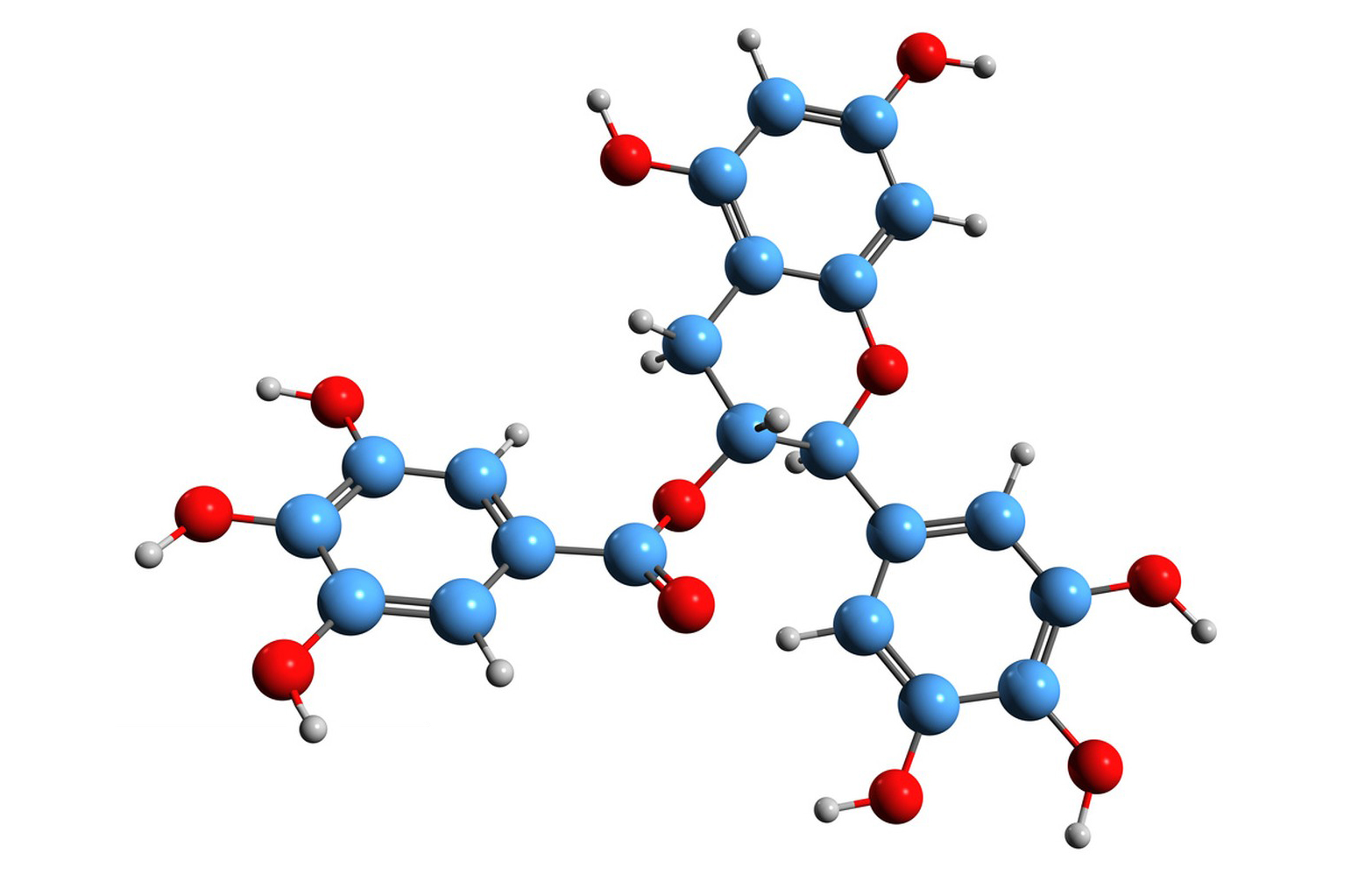
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is a type of catechin, which is a class of flavonoids. EGCG is particularly abundant in green tea, and it is one of the major polyphenols found in tea leaves. Green tea is derived from the Camellia sinensis plant, and the leaves undergo minimal oxidation during processing, preserving the natural compounds, including EGCG.
EGCG has been studied for its potential health benefits and is known for its antioxidant properties. It is believed to have various health-promoting effects, including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Additionally, EGCG has been associated with potential benefits for cardiovascular health and weight management.
The extraction process of EGCG
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is a catechin, a type of natural phenol and antioxidant, found in green tea. The extraction process of EGCG involves obtaining it from green tea leaves. Here is a general overview of the extraction process:
1.Harvesting Green Tea Leaves:
The process begins with the harvesting of fresh green tea leaves. The quality of the leaves can impact the final concentration of EGCG.
2.Withering:
The harvested leaves are spread out to wither, allowing them to lose moisture. This step is crucial for preparing the leaves for further processing.
3.Rolling:
The withered leaves are rolled to break down their cell walls. This rolling action helps release enzymes that initiate oxidation.
4.Oxidation (Fermentation):
Unlike black tea, green tea undergoes minimal oxidation. The oxidation process is halted by applying heat (usually by steaming or pan-frying) to the leaves. This step is essential to preserve the natural compounds, including EGCG.
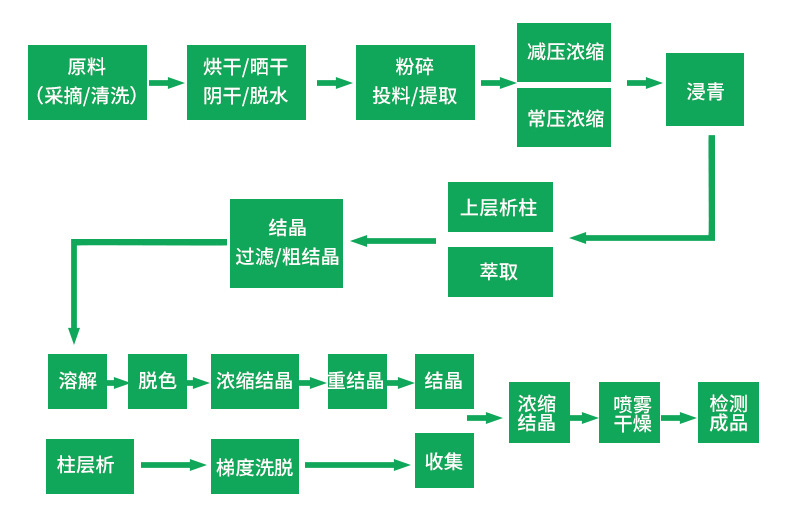
5.Drying:
The tea leaves are then dried to remove any remaining moisture. This helps in the preservation of the active compounds, including EGCG.
6.Extraction:
The dried tea leaves are subjected to an extraction process to isolate the desired components, including EGCG. Extraction methods may involve the use of solvents, such as water or organic solvents, to separate the bioactive compounds from the plant material.
7.Purification:
The extracted material is often purified to isolate EGCG further. Purification processes may include techniques like chromatography.
8.Concentration:
The purified EGCG may undergo concentration processes to increase its potency.
9.Formulation:
The final step involves formulating the EGCG extract into different products, such as supplements or cosmetic ingredients.
It’s important to note that the specific extraction methods can vary, and researchers and manufacturers may employ different techniques to obtain high-quality EGCG. Additionally, the extraction process should be carefully controlled to ensure the preservation of the beneficial properties of EGCG.
