Boron Nitride (BN) is a fascinating compound composed of boron (B) and nitrogen (N) atoms. It shares many structural similarities with carbon materials (like graphite and diamond), which gives it a range of unique physical properties depending on its form.
Chemical Structure of Boron Nitride
- Chemical Formula: Boron Nitride
- Molar Mass: 24.82 g/mol
- Bond Type: Covalent (strong Boron Nitride bonds with partial ionic character due to electronegativity difference)
Boron Nitride exists in several crystalline forms (polymorphs) analogous to carbon allotropes:
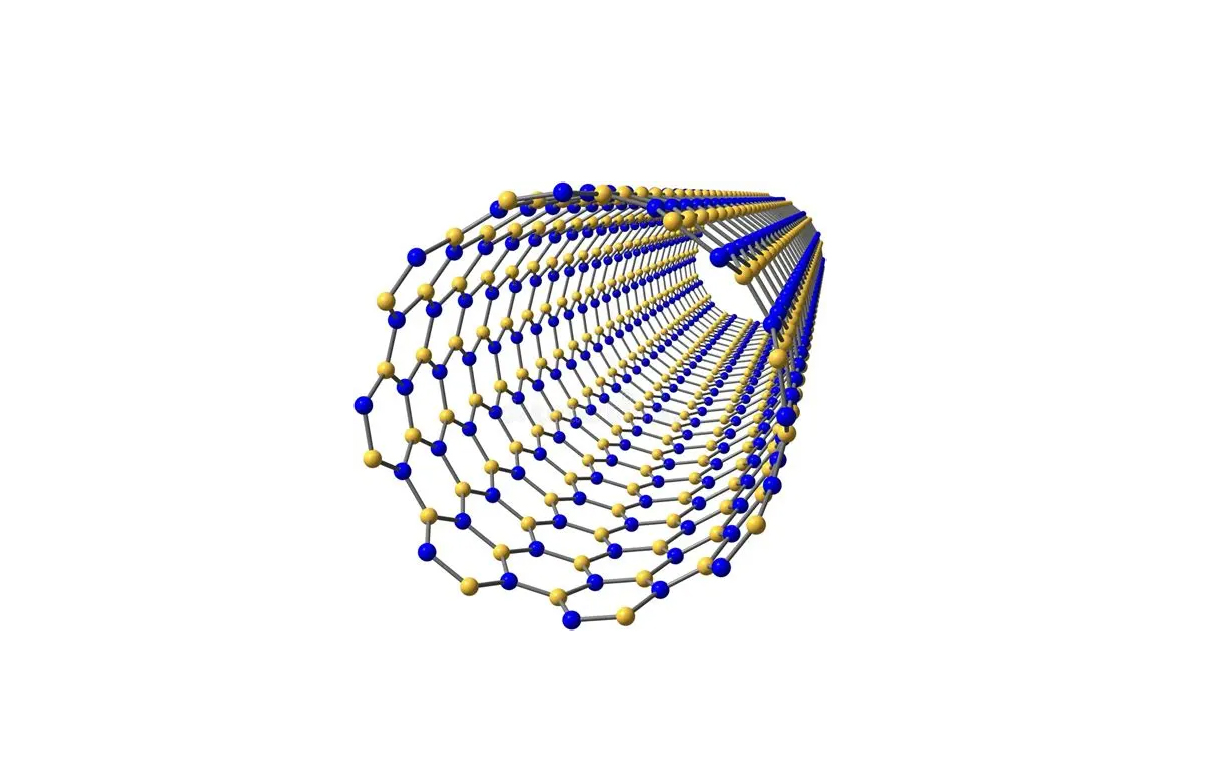
1. Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN):
- Structure similar to graphite.
- Each boron atom is covalently bonded to three nitrogen atoms in a hexagonal plane.
- Layers are held together by weak van der Waals forces.
- Bond length: ~1.45 Å (similar to graphite C–C bond).
2. Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN):
- Structure similar to diamond.
- Each atom (B and N) is tetrahedrally bonded (sp³ hybridized).
- Very hard material — second only to diamond.
3. Wurtzite Boron Nitride (w-BN):
- Structure similar to wurtzite (ZnS).
- Exists under high pressure; also superhard, potentially harder than diamond.
4. Amorphous Boron Nitride (a-BN):
- Non-crystalline, random atomic arrangement.
- Usually formed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or sputtering.
Physical Properties of Boron Nitride
| Property | Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) | Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN) | Wurtzite Boron Nitride (w-BN) |
| Appearance | White, soft, lubricating powder | Transparent, hard crystal | Transparent or opaque crystal |
| Crystal structure | Hexagonal (graphite-like) | Cubic (diamond-like) | Hexagonal (wurtzite-type) |
| Density | ~2.1 g/cm³ | ~3.48 g/cm³ | ~3.45 g/cm³ |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 1–2 | ~9.5 (next to diamond) | ~10 (theoretical) |
| Melting point | ~2973 °C (sublimes) | ~2973 °C | Similar |
| Thermal conductivity | High in-plane (up to 400 W/m·K) | High (~740 W/m·K) | High |
| Electrical conductivity | Insulator (bandgap ~5.9 eV) | Insulator/semiconductor | Insulator |
| Chemical stability | Chemically inert, oxidation resistant up to ~1000 °C in air | Very stable; resists oxidation up to ~1300 °C | Very stable |
| Color | White | Transparent (colorless) | Transparent |

Summary
Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) → “White graphite,” lubricating, thermally conductive, and electrically insulating.
Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN) → “Artificial diamond,” extremely hard, ideal for cutting and abrasive tools.
Wurtzite Boron Nitride (w-BN) → Rare, high-pressure phase, potentially harder than diamond.
Would you like me to include a labeled diagram of the crystal structures (hexagonal and cubic Boron Nitride) to visualize their differences?
