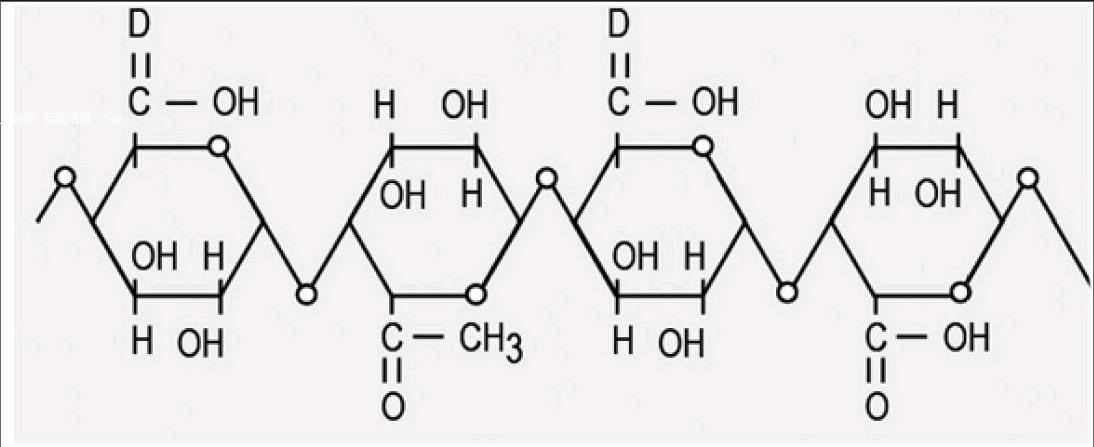
Citrus pectin—extracted from the peels and pulp of citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, and limes—has a wide range of applications across food, pharmaceutical, industrial, and health sectors.
(1) Food & Beverage Industry
Citrus pectin is most widely used as a gelling, thickening, and stabilizing agent.
Common applications
1. Jams and jellies
Forms a gel structure when mixed with sugar and acid.
2. Fruit preparations & fillings
Enhances texture and prevents separation.
3. Yogurts & dairy drinks
Improves viscosity and stabilizes protein.
4. Juices and beverages
Acts as a clouding agent, providing a natural mouthfeel.
5. Confectionery (candies, gummies)
Provides elasticity and controlled firmness.
(2) Dietary Supplements & Functional Foods
Citrus pectin—especially modified citrus pectin (MCP)—is popular for potential health benefits.
Uses
1. Cholesterol management
Binds bile acids, helping lower LDL cholesterol.
2. Digestive health
Acts as a soluble fiber and prebiotic.
3. Blood sugar control
Slows carbohydrate absorption.
4. Detoxification
MCP may bind heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and cadmium.
5. Immune support
MCP is studied for anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties.
(3) Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications
Citrus pectin is used for controlled drug release and health support.
Examples
1. Drug delivery systems
Forms gels and films for slow-release medication.
2. Wound healing materials
Used in hydrogels and medical dressings.
3. Cancer research
MCP is being investigated for inhibition of metastasis by blocking galectin-3.
(4) Cosmetics & Personal Care Products
Pectin functions as a natural stabilizer and humectant.
Uses
Lotions and creams – improves viscosity and stability
Shampoos and conditioners – enhances texture
Face masks and gels – forms smooth, hydrating films
(5) Industrial Applications
Thanks to its binding and film-forming properties:
1. Biodegradable packaging
Pectin-based films are explored as eco-friendly alternatives to plastic.
2. Adhesives & coatings
Used for natural, non-toxic formulations.
3. Textile printing
Acts as a thickener for dyes and printing pastes.
(6) Household & Culinary Uses
Home canning – making jams/jellies
Thickening soups, sauces, and desserts
Vegan/vegetarian gelling agent
A plant-based alternative to gelatin
Summary Table
| Sector | Key Uses |
| Food | Gelling, thickening, stabilizing |
| Supplements | Fiber support, detox, cholesterol, immune benefits |
| Medical | Drug delivery, wound dressing, anti-cancer research |
| Cosmetic | Texture improvement, hydration |
| Industrial | Biodegradable films, coatings, adhesives |
