Bifida Ferment Lysate is a biologically active ingredient derived from the fermentation of the probiotic bacteria Bifidobacterium. Essentially, it is the lysate—the broken-down components—of these bacteria, which contain beneficial metabolites, proteins, and other bioactive compounds. It’s widely used in skincare and cosmetics for its protective and restorative properties.
Definition
Bifida Ferment Lysate is obtained by fermenting Bifidobacterium (a beneficial probiotic bacterium) and then breaking down (lysing) the bacterial cells. The resulting lysate contains bioactive components, not live bacteria.
INCI Name
Origin
- Derived from Bifidobacterium species
- Produced through controlled microbial fermentation followed by cell lysis and purification

Key Components
The lysate typically contains:
- Peptides and amino acids
- Polysaccharides
- Nucleotides
- Organic acids
- Cell wall fragments
These components interact beneficially with the skin.
Main Functions in Skincare
- Strengthens the skin barrier by supporting repair mechanisms
- Improves skin resilience against environmental stress (UV, pollution)
- Soothes sensitive or irritated skin
- Enhances hydration retention
- Supports skin microbiome balance
- Anti-aging support by promoting DNA repair and reducing oxidative stress
Characteristics
- Non-living (safe and stable in formulations)
- Water-soluble
- Suitable for sensitive skin
- Compatible with most cosmetic formulations
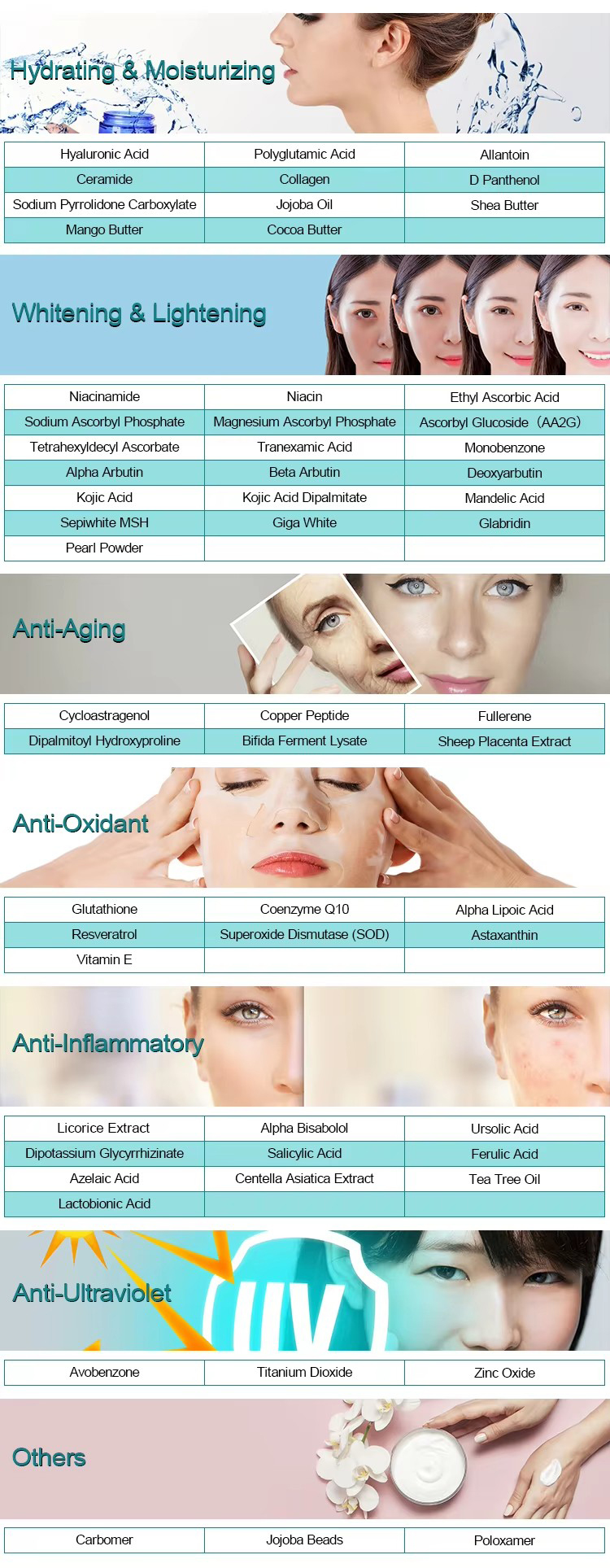
Common Applications
- Serums and essences
- Moisturizers and creams
- Repairing or post-procedure skincare
- Anti-aging and sensitive-skin products
Summary
Bifida Ferment Lysate is a bioactive postbiotic ingredient that helps repair, protect, and strengthen the skin, making it a popular choice in high-performance and dermatological skincare formulations.
If you’d like, I can also explain its mechanism of action, comparison with other ferments (like Galactomyces), or recommended usage levels in formulations.
