5-Deazaflavin is a derivative of flavin, where the nitrogen atom at position 5 replaces the carbon typically found in the flavin structure. It is a heterocyclic compound that plays a role in biological redox reactions and is often used in biochemistry and medicinal chemistry. Here are the chemical structure and physical properties of 5-Deazaflavin:
Chemical Structure of 5-Deazaflavin:
5-Deazaflavin has a structure similar to flavin mononucleotide (FMN) but with a nitrogen atom at position 5 of the isoalloxazine ring instead of a carbon. The structure consists of a tricyclic isoalloxazine ring system with nitrogen replacing the carbon atom at the 5 position.
- Chemical formula: C13H8N4O2
- IUPAC name: 5-Deaza-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]quinazoline-1,4-dione
- CAS number: 18493-07-9
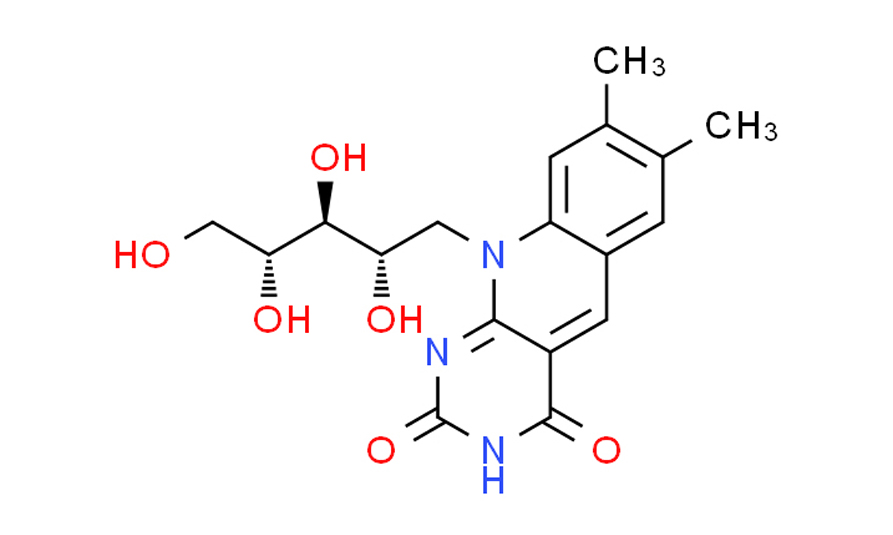
The structure consists of:
- A pteridine ring (a fused 6-membered and 5-membered ring system).
- A benzene ring fused to the pteridine ring.
- A keto group (C=O) at the 2- and 4-positions on the pteridine ring.
- A methyl group at the 6- and 7-positions on the pteridine ring.
Physical Properties of 5-Deazaflavin:
- Molecular weight: 256.24 g/mol
- Appearance: It typically appears as a yellow powder or crystalline solid.
- Melting point: It has a melting point around 290°C (dec.).
- Solubility: It is generally soluble in organic solvents such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and ethanol but less soluble in water.
- Absorption: As with flavins, 5-Deazaflavin exhibits characteristic absorption in the UV-visible range, typically around 370–450 nm due to the conjugated ring system.
Biological Activity:
5-Deazaflavin acts similarly to flavins in biochemical reactions, particularly in redox processes, and can serve as an electron carrier in enzymatic reactions. It is sometimes used as a coenzyme model in studies of flavin-dependent enzymes.
If you’re interested in a detailed molecular representation or additional information on its uses, let me know!
