Bacillus pumilus is a species of bacteria that belongs to the genus Bacillus, which is commonly found in soil, water, and various environments worldwide. It is considered a beneficial microorganism due to its numerous functions and potential applications in different fields. Here are some of the functions and benefits of Bacillus pumilus:

Biodegradation: Bacillus pumilus possesses the ability to break down complex organic compounds, contributing to the process of biodegradation. This capability is essential in reducing environmental pollution caused by various contaminants.
Biocontrol: Some strains of Bacillus pumilus have been found to exhibit antagonistic properties against certain plant pathogens, insects, and nematodes. As a result, they can be used as biocontrol agents in agriculture to help manage pest and disease problems without relying on harmful chemical pesticides.
Industrial applications: Bacillus pumilus produces various enzymes, including proteases, lipases, amylases, and cellulases, which have significant industrial applications. These enzymes can be utilized in food processing, detergent manufacturing, and other industrial processes.
Environmental remediation: Due to its ability to degrade pollutants and toxins, Bacillus pumilus shows promise in environmental remediation efforts. It can be used to clean up contaminated sites and support the restoration of ecosystems affected by pollutants.
Probiotic potential: Some strains of Bacillus pumilus have shown probiotic properties, meaning they can positively influence the gut microbiota and promote digestive health in animals and humans. Probiotics can help improve nutrient absorption, strengthen the immune system, and aid in preventing certain gastrointestinal disorders.

Production of antimicrobial compounds: Bacillus pumilus can produce antimicrobial compounds, such as bacteriocins, which are natural substances that inhibit the growth of specific harmful bacteria. These compounds have potential applications in food preservation and as an alternative to traditional antibiotics.
Bioremediation: Bacillus pumilus has been explored for its potential in bioremediation, which involves the use of microorganisms to clean up oil spills and other hydrocarbon-contaminated environments.
It is important to note that while Bacillus pumilus has several beneficial characteristics, not all strains are safe or suitable for all applications. Some strains might cause infections in immunocompromised individuals, so proper risk assessment and selection of safe strains are essential when using Bacillus pumilus in various applications. Additionally, it’s essential to follow recommended guidelines and regulations to ensure the safe and effective use of Bacillus pumilus-based products.
Base ingredient of Bacillus Pumilus
Bacillus pumilus is a species of bacteria that belongs to the Bacillus genus. The base ingredient, or you can say the primary constituent of Bacillus pumilus, is a single-celled microorganism belonging to the domain Bacteria. It is a Gram-positive bacterium, which means it retains the crystal violet stain during the Gram staining process. This bacterium is known for its ability to form endospores, which are highly resistant structures that allow the organism to survive harsh environmental conditions.
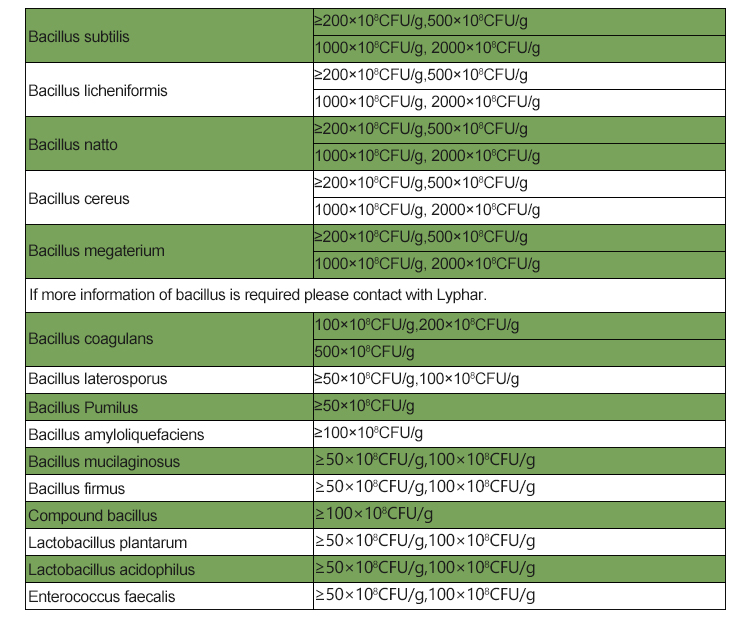
The complete composition of Bacillus pumilus includes various biomolecules, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and other cellular components, just like any other bacterial species. The specific functions and characteristics of Bacillus pumilus can vary based on the environment in which it is found and the genes it expresses.
Bacillus pumilus can be found in various environments, including soil, water, and even in some industrial settings. Some strains of Bacillus pumilus have been studied for their potential applications in biotechnology, enzyme production, and as biopesticides due to their ability to produce various enzymes and secondary metabolites.
