As of my last update in September 2021, Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is not used as a standalone treatment for medical conditions. ATP is a molecule that plays a crucial role in cellular energy transfer and is essential for various physiological processes within the body. It serves as the primary source of energy for cellular functions.
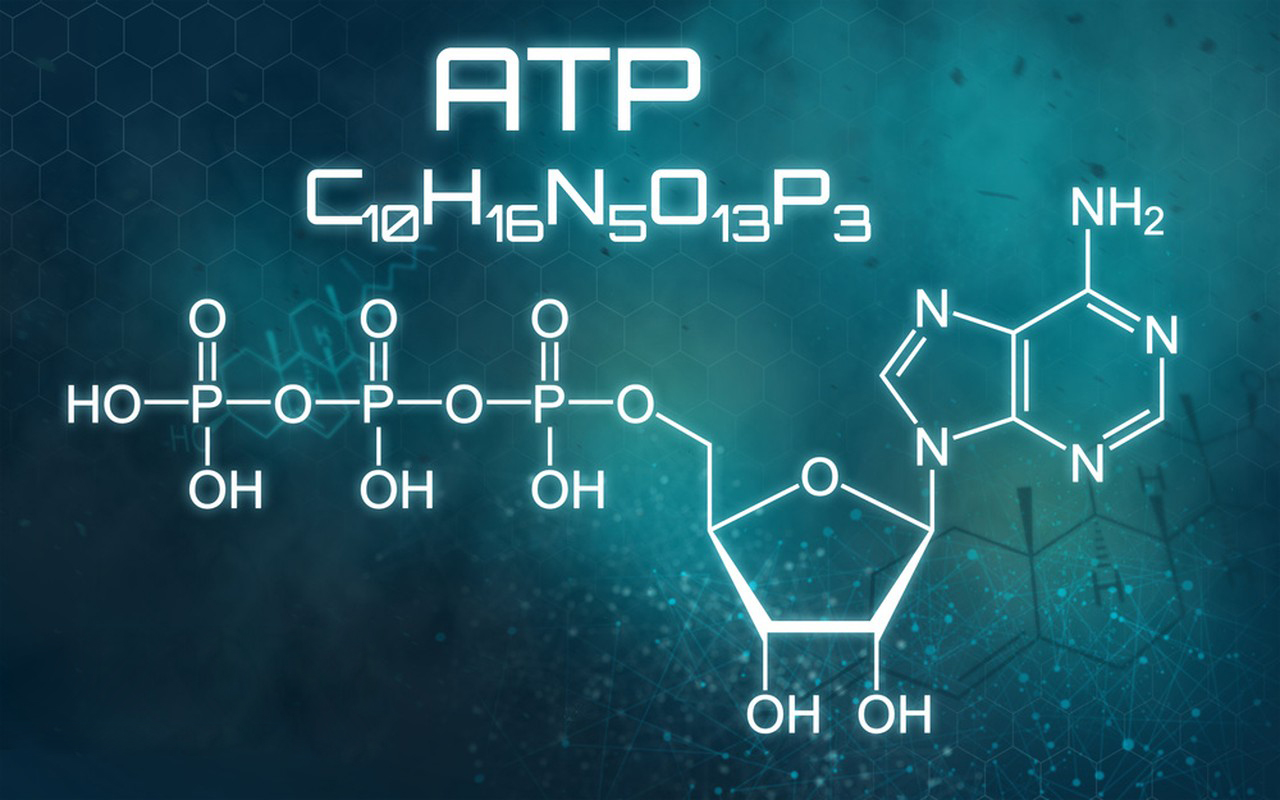
However, ATP itself is not administered as a medication or treatment. Instead, medical treatments may involve targeting specific conditions or diseases that affect ATP production, utilization, or cellular metabolism. For example:
1.Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): Some treatments for CFS may focus on improving mitochondrial function, as mitochondria are responsible for producing ATP in cells. Therapies might include lifestyle changes, exercise, and specific medications.
2.Cardiovascular Conditions: In cases of heart-related conditions like heart failure or arrhythmias, treatment may aim to improve the heart’s efficiency in generating ATP for proper function. Medications, lifestyle changes, and cardiac rehabilitation are common approaches.
3.Wound Healing: Some studies have explored the use of ATP-based therapies to promote wound healing. These treatments may involve using substances that release ATP at the wound site to enhance the healing process. However, the clinical use of such therapies is still limited and experimental.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for up-to-date information on treatments and their effectiveness for specific medical conditions. Medical research is continually evolving, and new treatments may have emerged since my last update.
Efficacy evaluation of Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that serves as the primary energy carrier in cells. It plays a critical role in various biological processes and is essential for the functioning of living organisms. When it comes to evaluating the efficacy of ATP, there are several aspects to consider:
1.Cellular Energy Production: ATP is involved in cellular respiration, where it acts as an energy currency. During processes like glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, ATP is synthesized and broken down to provide energy for cellular activities. The efficacy of ATP can be measured by its ability to efficiently produce and transfer energy within cells.
2.Biological Functions: ATP is required for a wide range of biological functions, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, active transport of molecules across cell membranes, and synthesis of biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids. The efficacy of ATP can be evaluated by its ability to support these fundamental biological processes.
3.Mitochondrial Function: The majority of cellular ATP is produced in the mitochondria through oxidative phosphorylation. Evaluating ATP’s efficacy can involve assessing mitochondrial health and function, as any disruptions in these processes can impact ATP production and cellular energy balance.
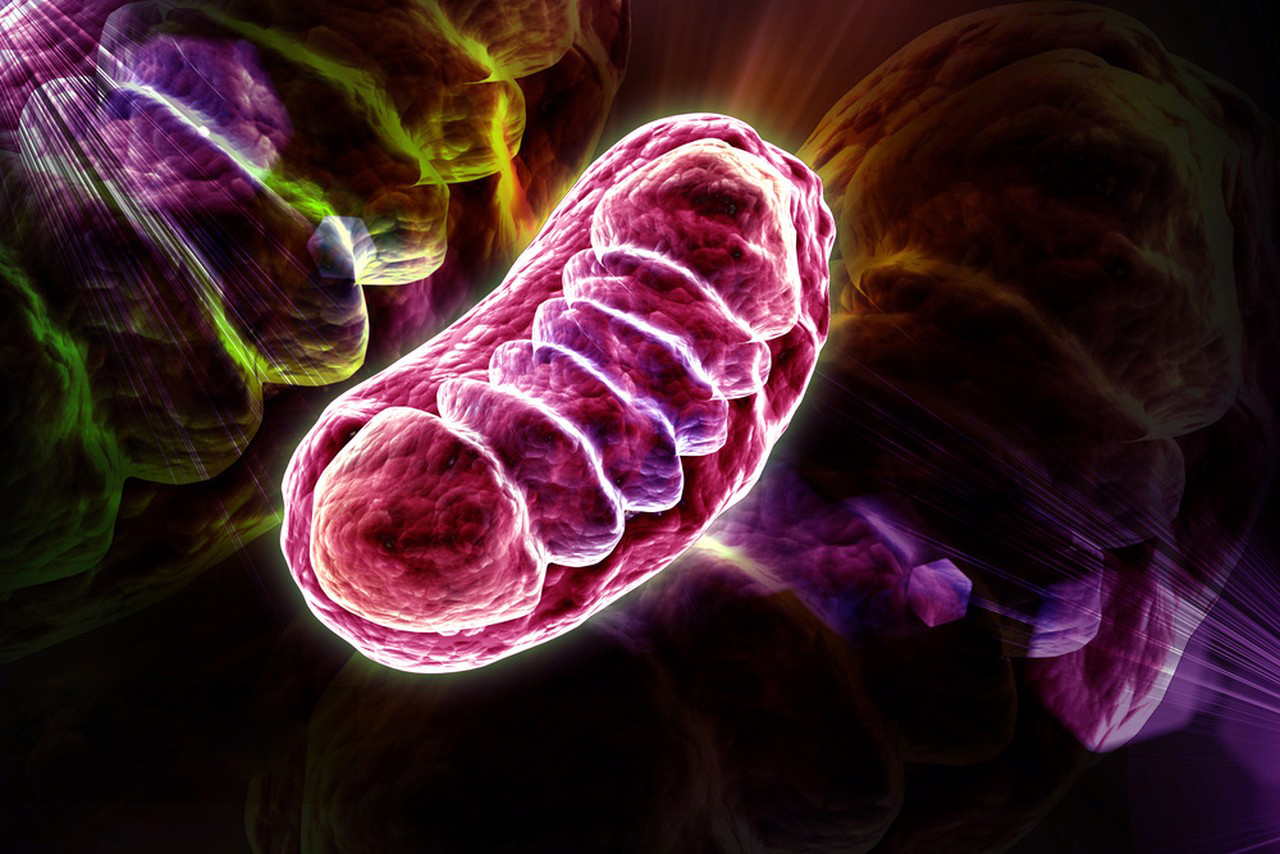
4.Drug and Pharmaceutical Testing: In the context of drug development, the efficacy of certain medications can be evaluated based on their impact on ATP production and utilization. For instance, drugs that target mitochondrial function or ATP synthesis may be assessed for their effects on overall cellular energy levels.
5.ATP Testing: There are specific biochemical assays available to directly measure ATP levels in cells and tissues. These tests can provide quantitative data on ATP content, which can be useful in assessing cellular health and energy status.
6.Exercise Performance: ATP is critical for muscle contraction during physical activities. Evaluating the efficacy of ATP in the context of exercise performance can involve studying factors like ATP turnover, fatigue resistance, and recovery rates.
7.Disease States: Certain diseases and medical conditions can affect ATP production and utilization. Evaluating ATP efficacy in these contexts may involve studying how these conditions impact cellular energy balance and whether interventions can restore ATP levels.
Overall, the efficacy evaluation of ATP is a complex process that involves understanding its role in cellular energy production and various biological functions. It requires a combination of biochemical, cellular, and physiological assessments to gain a comprehensive understanding of ATP’s performance in different contexts.
