5-Amino-1MQ Iodide is a derivative of 1-Methylquinolinium (1MQ) with emerging interest in the fields of metabolic regulation, weight loss, and mitochondrial function. Below is a comprehensive study covering its structure, mechanism of action, potential benefits, risks, and ongoing research.
1. Chemical Structure and Properties
- Chemical Name: 5-Amino-1MQ Iodide
- Molecular Formula: C10H11IN2
- Molecular Weight: Varies depending on salt form
- Solubility: Typically water-soluble due to its iodide salt form
- Chemical Class: Quinoline derivative

2. Mechanism of Action
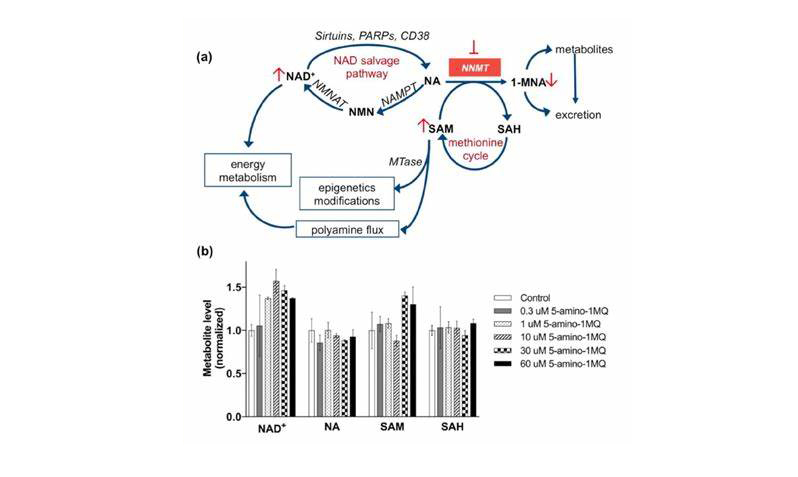
5-Amino-1MQ Iodide acts as an inhibitor of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), an enzyme involved in cellular energy metabolism. NNMT plays a key role in:
- Regulating the availability of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD⁺), which is crucial for mitochondrial function and cellular energy balance.
- Modulating methylation reactions, affecting metabolic pathways related to obesity and insulin resistance.
By inhibiting NNMT:
- NAD⁺ levels increase, leading to enhanced Sirtuin (SIRT1) activation, which improves mitochondrial efficiency and fat metabolism.
- Fat cell metabolism is upregulated, promoting lipolysis and reducing adipocyte size.
- Glucose metabolism improves, potentially benefiting individuals with metabolic disorders.
3. Potential Benefits
3.1 Weight Loss and Fat Reduction
- NNMT inhibition has been shown to reduce adiposity, particularly in animal models of obesity.
- Increased energy expenditure without necessarily increasing food intake.
3.2 Muscle Function and Mitochondrial Health
- Enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis, improving energy production and endurance.
- Potential role in muscle repair and aging-associated muscle decline (sarcopenia).
3.3 Metabolic Disorders (Diabetes, Insulin Sensitivity)
- Improved insulin sensitivity through enhanced NAD⁺ availability.
- Reduction in glucose levels, suggesting potential benefits in managing Type 2 Diabetes.
3.4 Longevity and Anti-Aging Effects
- Increased SIRT1 activation has been linked to lifespan extension.
- Protection against oxidative stress via enhanced mitochondrial function.
4. Potential Risks and Side Effects
Though limited human studies exist, potential concerns include:
- Overactivation of NAD⁺ pathways, possibly leading to excessive metabolic demand or unintended weight loss.
- Impact on methylation balance, which could affect DNA repair and epigenetic regulation.
- Possible thyroid disruption, as iodide plays a role in thyroid hormone synthesis.
Preclinical studies suggest minimal toxicity, but long-term human safety is not yet established.
5. Ongoing Research and Clinical Trials
5.1 Animal and Preclinical Studies
- Mouse models of obesity have shown significant reductions in fat mass and weight gain with 5-Amino-1MQ Iodide treatment.
- Metabolic studies indicate improved insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial function.
5.2 Human Trials
- Currently, no large-scale human clinical trials have been published.
- Some early-stage research and anecdotal reports suggest weight loss effects, but further controlled studies are needed.
6. Future Directions
- Human clinical trials to determine efficacy and safety at different dosages.
- Potential combination therapies, especially with NAD⁺ precursors (e.g., Nicotinamide Riboside).
- Exploring broader therapeutic applications, such as neurodegenerative diseases and cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
5-Amino-1MQ Iodide is a promising NNMT inhibitor with potential applications in weight loss, metabolic health, and mitochondrial function. While preclinical studies suggest efficacy, human research is still in its infancy, and further clinical trials are necessary to confirm its safety and effectiveness.
Would you like references to scientific literature or further insights into a specific aspect?
